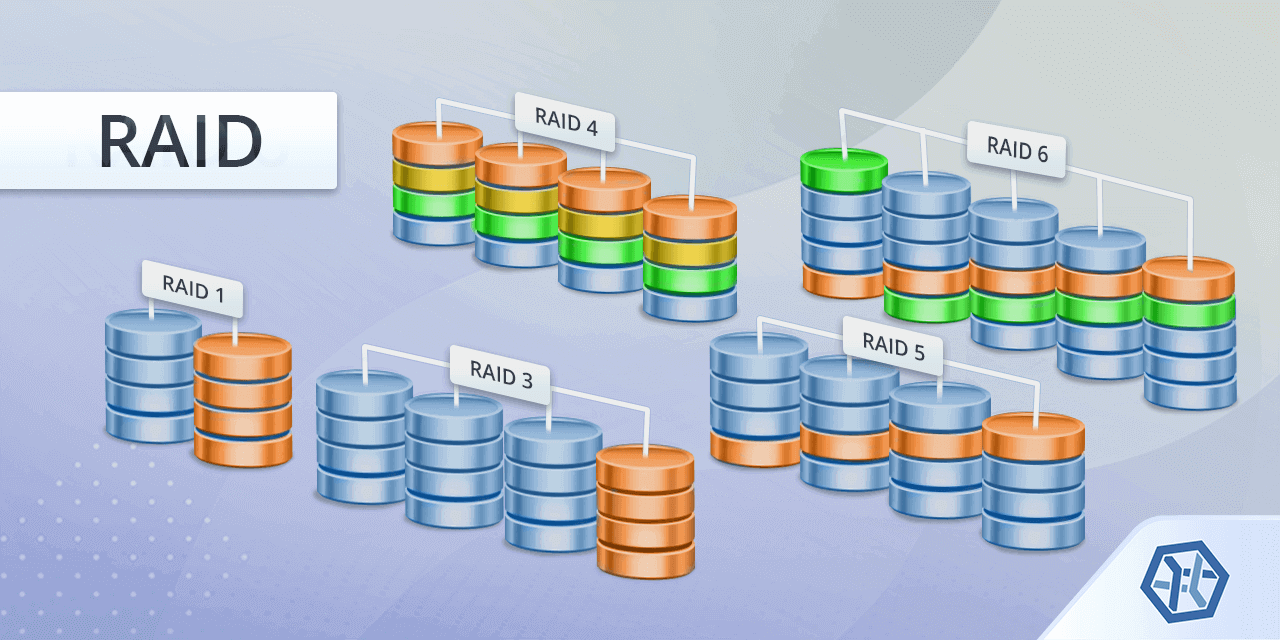
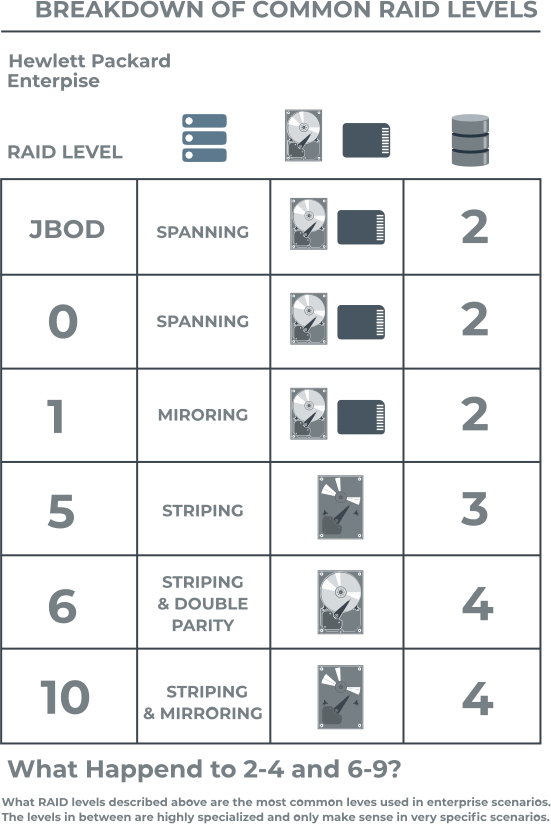
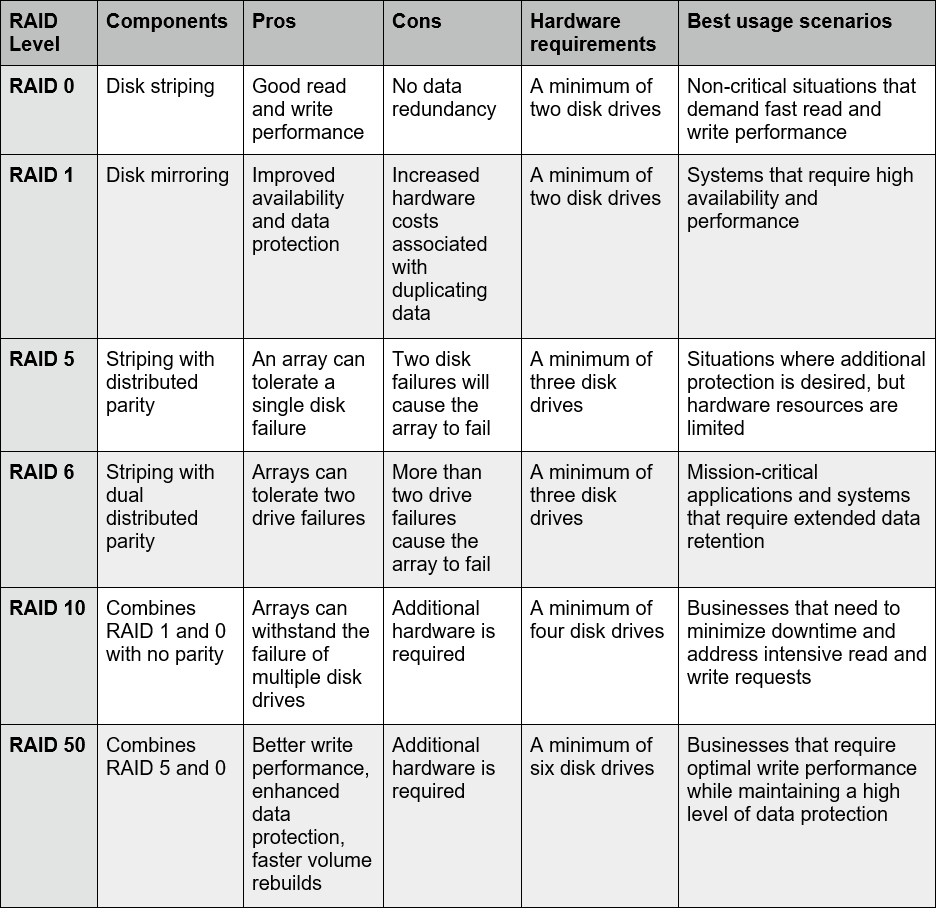
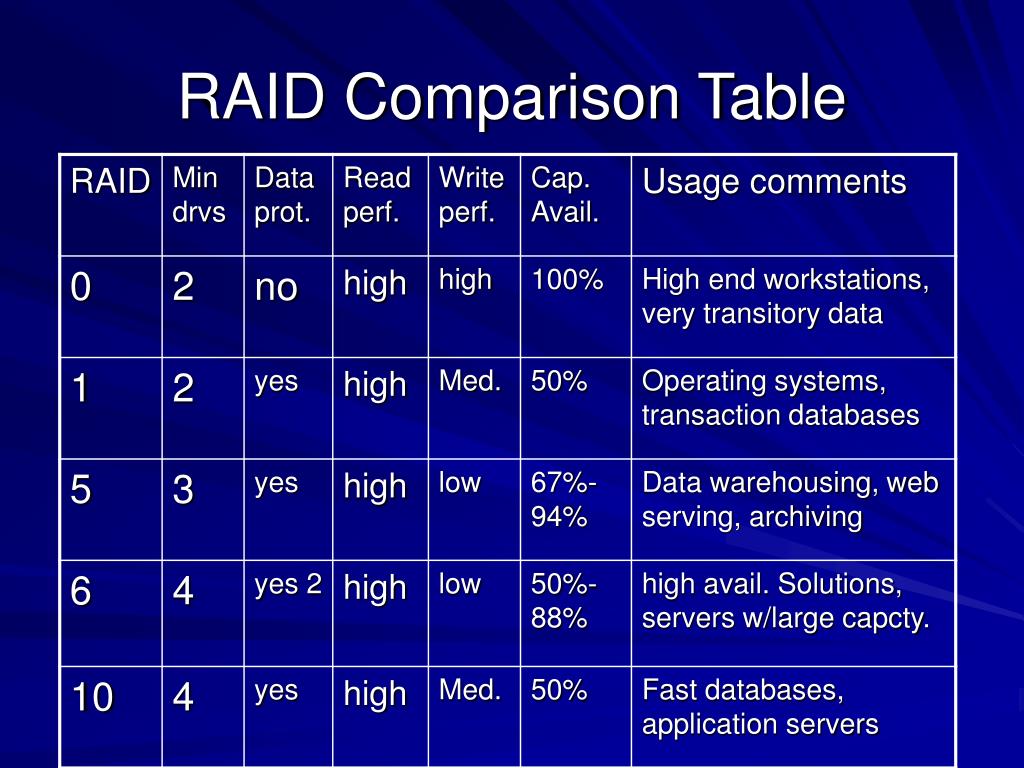
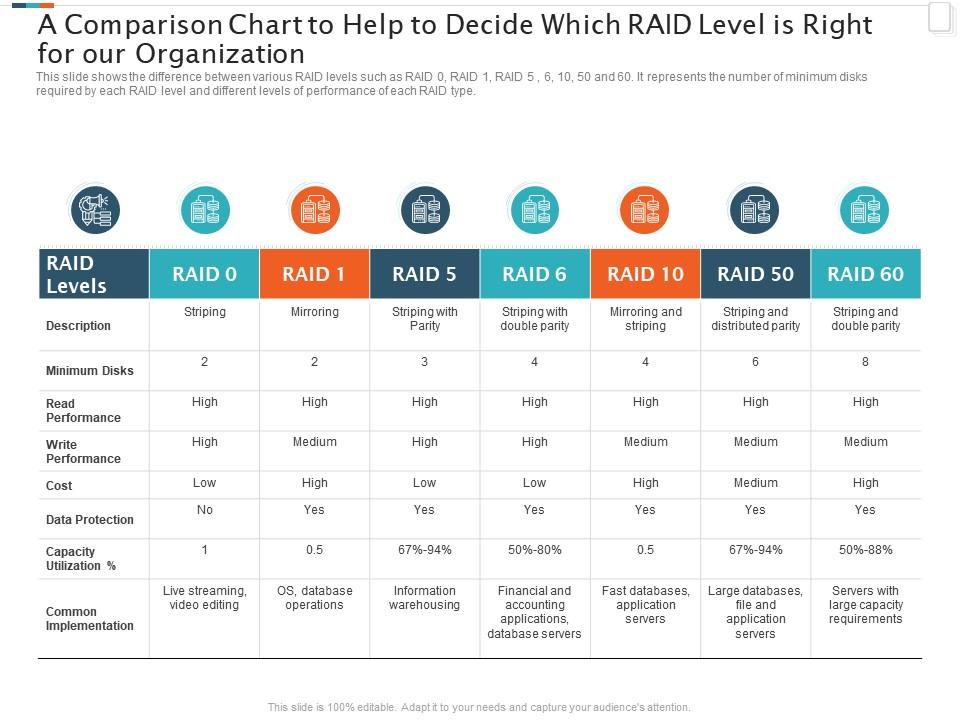
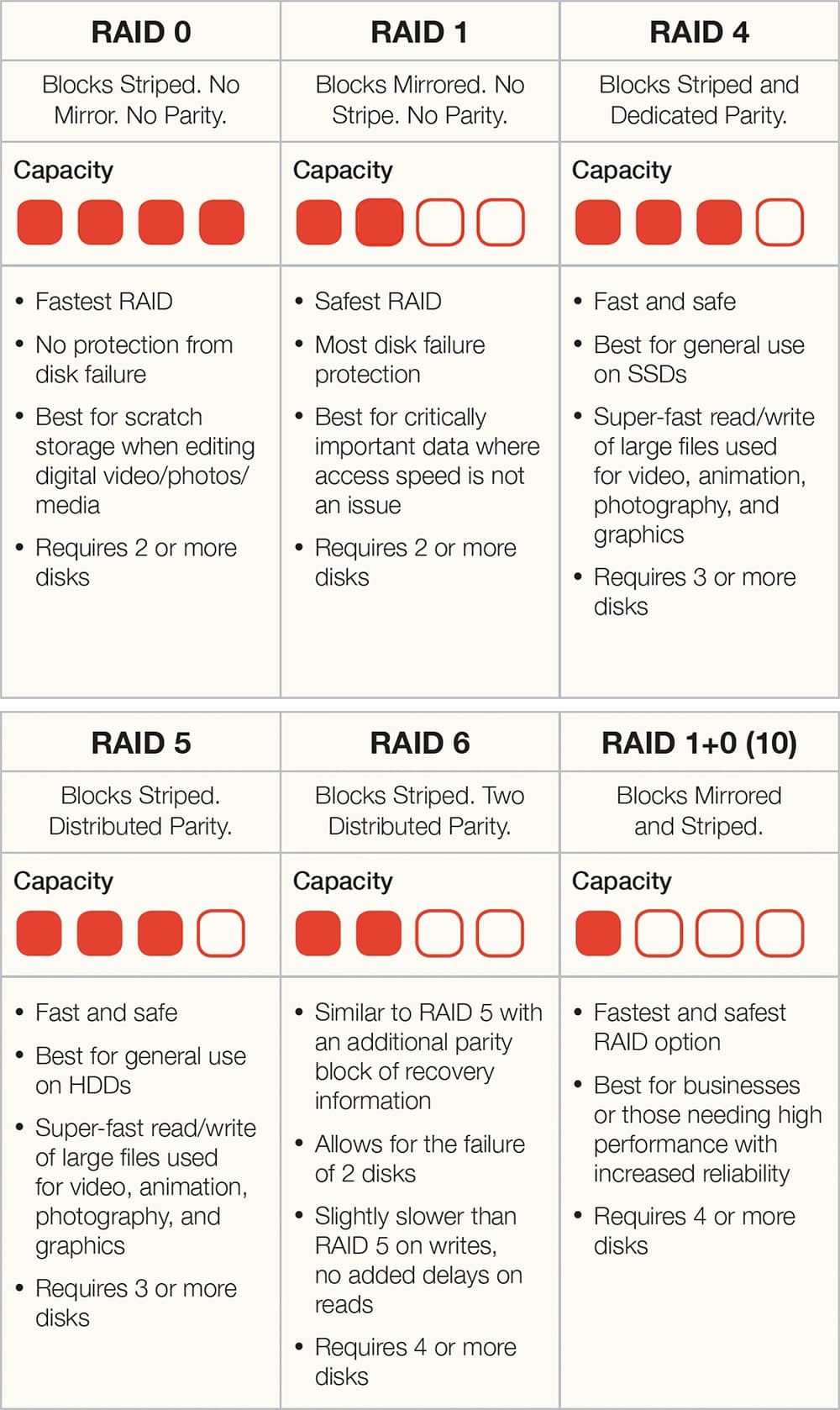
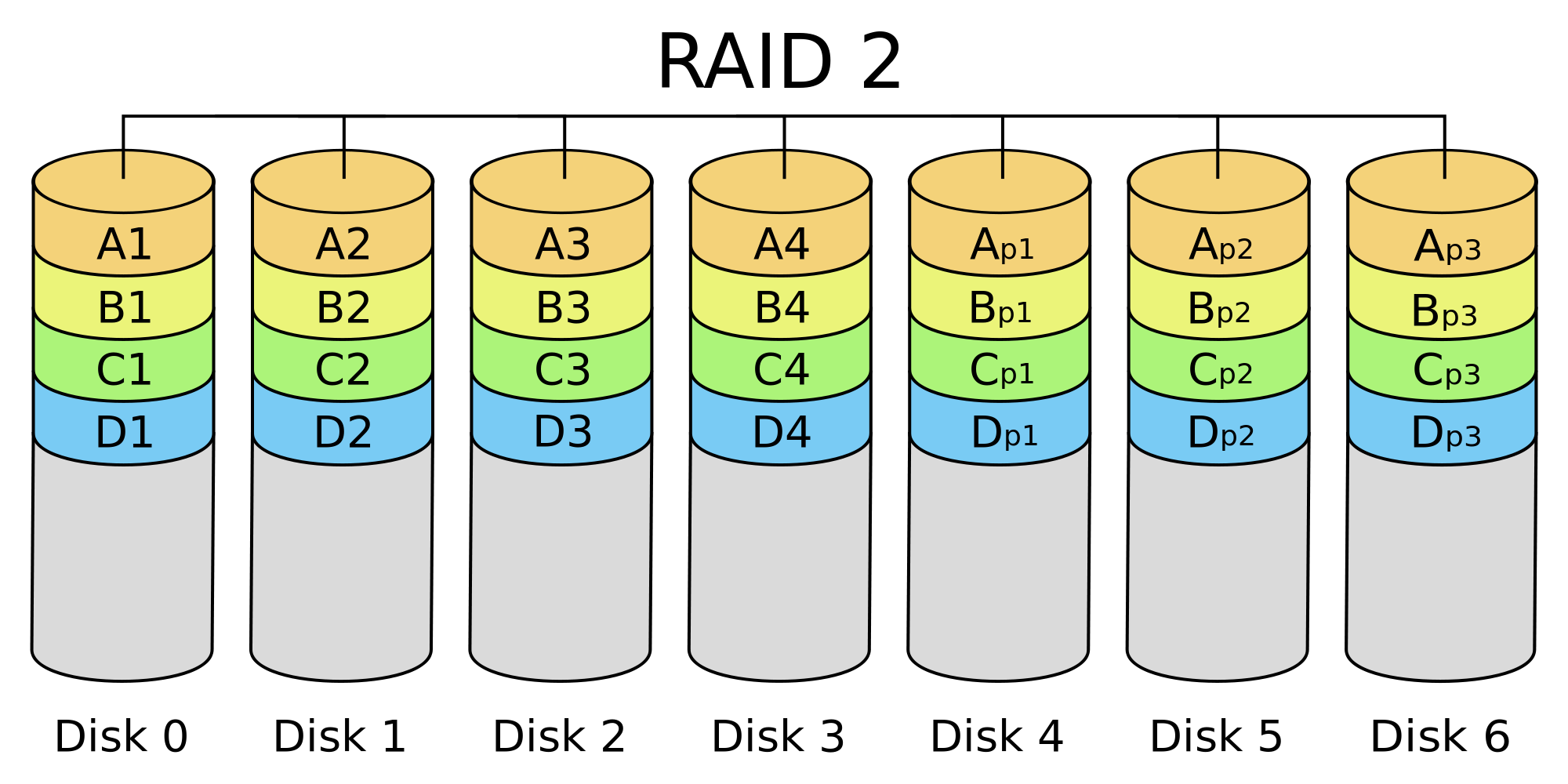
Raid Types Chart
Raid Types Chart - Raid levels are a way of combining multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. Different raid levels have different speed and fault tolerance properties. On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of raids. Raid arrays with different architectures can be similar, but. Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that integrates several separate drives for better storage performance and higher reliability. Raid levels can be broken into three categories: Learn about the different raid levels and how they work. These ways are called raid levels. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Learn about the different raid levels and how they work. Raid arrays with different architectures can be similar, but. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that integrates several separate drives for better storage performance and higher reliability. Raid stands for redundant array of inexpensive (independent) disks. Standard levels of raid are made up of the basic types of raid numbered 0 through 6. There are many different ways to organize data in a raid array. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Knowing the differences between raid types and setups is essential when planning a reliable storage. On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of raids. Raid uses different techniques to distribute data across drives. There are many different ways to organize data in a raid array. These ways are called raid levels. Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that integrates several separate drives for better storage performance and higher reliability. Multiple. These ways are called raid levels. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storage Raid arrays with different architectures can be similar, but. Different raid levels have different speed and fault tolerance properties. On most situations you will be using. Different raid levels have different speed and fault tolerance properties. Raid uses different techniques to distribute data across drives. Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. There are many different ways to organize data in a raid array. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the. There are many different ways to organize data in a raid array. Raid stands for redundant array of inexpensive (independent) disks. Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. These ways are called raid levels. On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of raids. There are many different ways to organize data in a raid array. Standard levels of raid are made up of the basic types of raid numbered 0 through 6. Raid arrays with different architectures can be similar, but. Raid levels are a way of combining multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. These ways are called raid levels. Raid levels can be broken into three categories: Raid arrays with different architectures can be similar, but. The most common types are raid 0 (striping), raid 1 (mirroring) and its variants, raid 5 (distributed parity), and raid 6 (dual parity). Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. Learn about the. Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. Learn about the different raid levels and how they work. The most common types are raid 0 (striping), raid 1 (mirroring) and its variants, raid 5 (distributed parity), and raid 6 (dual parity). Raid arrays with different architectures can be similar, but. Short. Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. Raid stands for redundant array of inexpensive (independent) disks. Different raid levels have different speed and fault tolerance properties. On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of raids. Raid levels can be broken into three categories: There are many different ways to organize data in a raid array. Standard levels of raid are made up of the basic types of raid numbered 0 through 6. Raid uses different techniques to distribute data across drives. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security. Learn about the different raid levels and how they work. Raid levels can be broken into three categories: Multiple raid levels can also be combined or. Raid uses different techniques to distribute data across drives. On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of raids. Raid uses different techniques to distribute data across drives. Raid (redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that integrates several separate drives for better storage performance and higher reliability. Raid stands for redundant array of inexpensive (independent) disks. There are many different ways to organize data in a raid array. These ways are called raid levels. Raid arrays with different architectures can be similar, but. The most common types are raid 0 (striping), raid 1 (mirroring) and its variants, raid 5 (distributed parity), and raid 6 (dual parity). On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of raids. Learn about the different raid levels and how they work. Raid levels can be broken into three categories: Raid functions are performed on a microprocessor located on the external raid controller independent of the host. Raid levels are a way of combining multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. Short tutorial on raid levels 0, 1, 5, 6 and 10, the advantages of striping, mirroring and parity for performance & security plus their use for prepress storageTypes Of Raid Levels With Diagrams Windowstechpro Com vrogue.co
RAID Levels And Types Explained Differences And Benefits, 44 OFF
Types Of Raid Levels With Diagrams Windowstechpro Com vrogue.co
RAID Levels Explained (2025) DiskInternals
Understanding Raid Levels
Understanding Raid Levels
Raid Speed Comparison Chart
Understanding Raid Levels
A Beginners Guide to Understanding RAID
Why Using RAID Is A Good Idea Digital Conqueror
Different Raid Levels Have Different Speed And Fault Tolerance Properties.
Knowing The Differences Between Raid Types And Setups Is Essential When Planning A Reliable Storage.
Multiple Raid Levels Can Also Be Combined Or.
Standard Levels Of Raid Are Made Up Of The Basic Types Of Raid Numbered 0 Through 6.
Related Post: