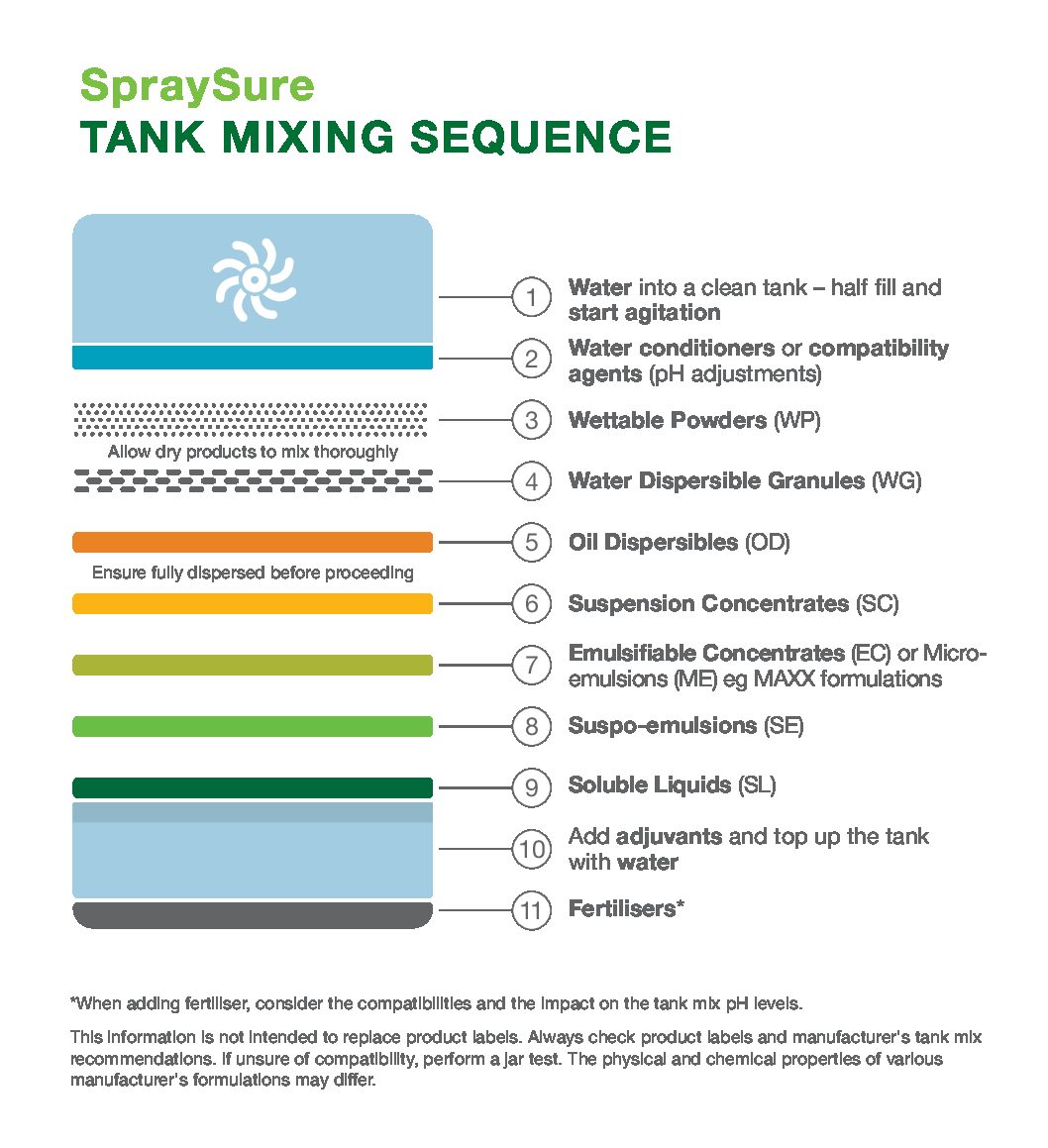
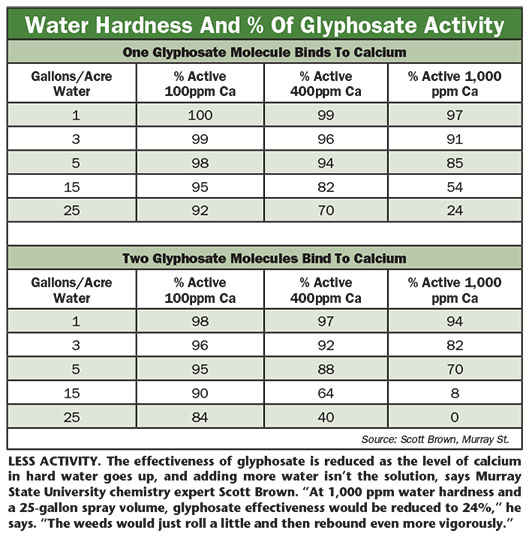
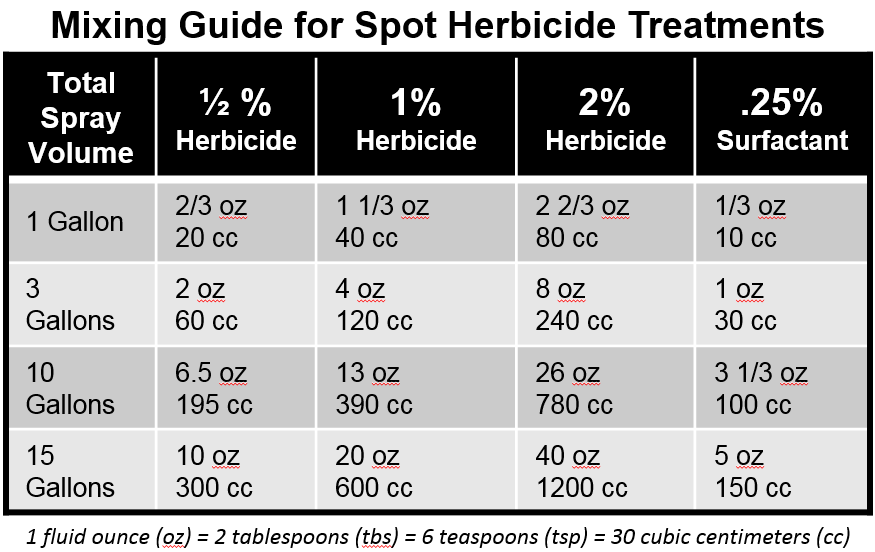
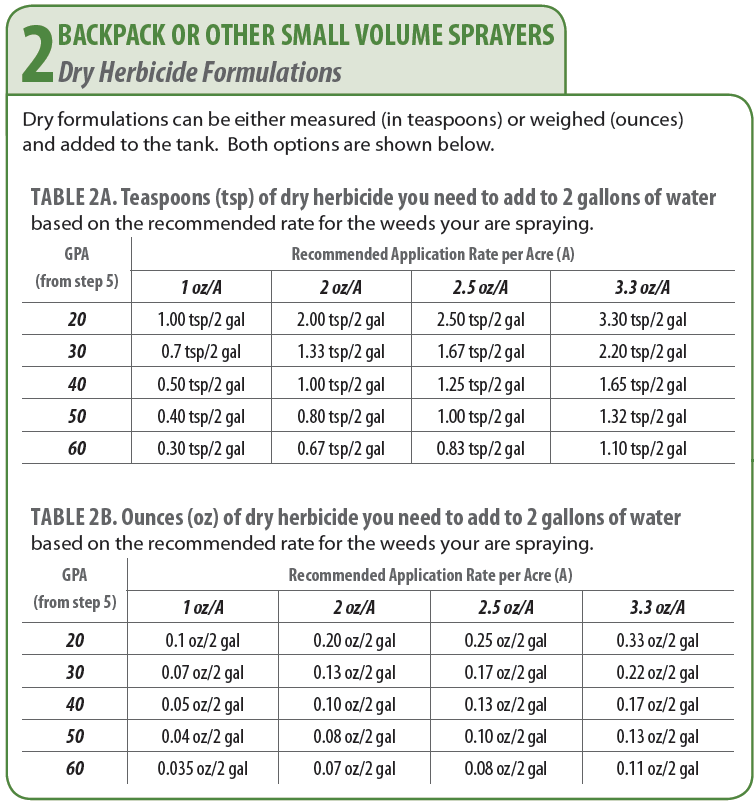
Herbicide Mixing Order Chart
Herbicide Mixing Order Chart - These herbicides will inhibit the photosynthesis process, and the plant. Learn how to choose the right herbicide for effective weed control. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals. In general, the herbicide must be applied to a larger surface of the leaves for a successful operation. Applying herbicides with multiple modes. Understanding a herbicide’s soa and moa can help farmers select effective herbicides against target weeds while reducing herbicide resistance risk. Upl is constantly working towards innovating to improve our. A herbicide is a type of pesticide designed to control or kill unwanted weeds, grasses, or plants in agricultural fields, gardens, landscapes, and other areas where. Herbicide a field after application of a herbicide weeds controlled with herbicide herbicides (us: Knowing how herbicides work and how to use them safely is important for both agricultural producers and home gardeners. This publication describes the symptoms of each. An herbicide is an agent, usually chemical, for killing or inhibiting the growth of unwanted plants, such as weeds, invasive species, or agricultural pests. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals. These herbicides will inhibit the photosynthesis process, and the plant. The most direct effects of herbicide pollution are decreased condition, growth, and reproduction, and increased mortality, of plants (i.e., macrophytes, periphyton and. Applying herbicides with multiple modes. Upl is constantly working towards innovating to improve our. A herbicide is a type of pesticide designed to control or kill unwanted weeds, grasses, or plants in agricultural fields, gardens, landscapes, and other areas where. Explore types, applications, and tips to protect crops and ensure sustainable farming. Herbicide a field after application of a herbicide weeds controlled with herbicide herbicides (us: Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals. Herbicide a field after application of a herbicide weeds controlled with herbicide herbicides (us: This publication describes the symptoms of each. Knowing how herbicides work and how to use them safely is important for both agricultural producers. In general, the herbicide must be applied to a larger surface of the leaves for a successful operation. Learn how to choose the right herbicide for effective weed control. A herbicide is a type of pesticide designed to control or kill unwanted weeds, grasses, or plants in agricultural fields, gardens, landscapes, and other areas where. Each herbicide type offers unique. Applying herbicides with multiple modes. A herbicide is a type of pesticide designed to control or kill unwanted weeds, grasses, or plants in agricultural fields, gardens, landscapes, and other areas where. Knowing how herbicides work and how to use them safely is important for both agricultural producers and home gardeners. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must. These herbicides will inhibit the photosynthesis process, and the plant. Herbicide a field after application of a herbicide weeds controlled with herbicide herbicides (us: This publication describes the symptoms of each. The most direct effects of herbicide pollution are decreased condition, growth, and reproduction, and increased mortality, of plants (i.e., macrophytes, periphyton and. An herbicide is an agent, usually chemical,. The most direct effects of herbicide pollution are decreased condition, growth, and reproduction, and increased mortality, of plants (i.e., macrophytes, periphyton and. Explore types, applications, and tips to protect crops and ensure sustainable farming. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals. A herbicide is. A herbicide is a type of pesticide designed to control or kill unwanted weeds, grasses, or plants in agricultural fields, gardens, landscapes, and other areas where. Learn how to choose the right herbicide for effective weed control. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals.. Explore types, applications, and tips to protect crops and ensure sustainable farming. These herbicides will inhibit the photosynthesis process, and the plant. Knowing how herbicides work and how to use them safely is important for both agricultural producers and home gardeners. This publication describes the symptoms of each. A herbicide is a type of pesticide designed to control or kill. In general, the herbicide must be applied to a larger surface of the leaves for a successful operation. Applying herbicides with multiple modes. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals. Knowing how herbicides work and how to use them safely is important for both. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals. This publication describes the symptoms of each. Upl is constantly working towards innovating to improve our. Herbicide a field after application of a herbicide weeds controlled with herbicide herbicides (us: These herbicides will inhibit the photosynthesis process,. Applying herbicides with multiple modes. An herbicide is an agent, usually chemical, for killing or inhibiting the growth of unwanted plants, such as weeds, invasive species, or agricultural pests. Herbicide a field after application of a herbicide weeds controlled with herbicide herbicides (us: Explore types, applications, and tips to protect crops and ensure sustainable farming. This publication describes the symptoms. The most direct effects of herbicide pollution are decreased condition, growth, and reproduction, and increased mortality, of plants (i.e., macrophytes, periphyton and. Each herbicide type offers unique benefits and considerations that must be evaluated based on the specific weed problems and agricultural or landscaping goals. Herbicide a field after application of a herbicide weeds controlled with herbicide herbicides (us: In general, the herbicide must be applied to a larger surface of the leaves for a successful operation. Learn how to choose the right herbicide for effective weed control. This publication describes the symptoms of each. A herbicide is a type of pesticide designed to control or kill unwanted weeds, grasses, or plants in agricultural fields, gardens, landscapes, and other areas where. Upl is constantly working towards innovating to improve our. Knowing how herbicides work and how to use them safely is important for both agricultural producers and home gardeners. An herbicide is an agent, usually chemical, for killing or inhibiting the growth of unwanted plants, such as weeds, invasive species, or agricultural pests. Understanding a herbicide’s soa and moa can help farmers select effective herbicides against target weeds while reducing herbicide resistance risk.Tank Mixing Sequence Product Resource Lawn Addicts
Herbicide Mixing Order Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Herbicide Mixing Order Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
10 Ways to Improve Pesticide Spray Coverage and Efficacy Pest Prophet Blog
Herbicide Mixing Order Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
PPT Herbicide Timing PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID140905
Chemical Mixing Order Chart at Genevieve Tarrant blog
The Cheapest Method to Control Pasture Weeds Panhandle Agriculture
herbicide mixing order chart Keski
Tank mixing order and the “Jar Test” Sprayers 101
Explore Types, Applications, And Tips To Protect Crops And Ensure Sustainable Farming.
Applying Herbicides With Multiple Modes.
These Herbicides Will Inhibit The Photosynthesis Process, And The Plant.
Related Post: