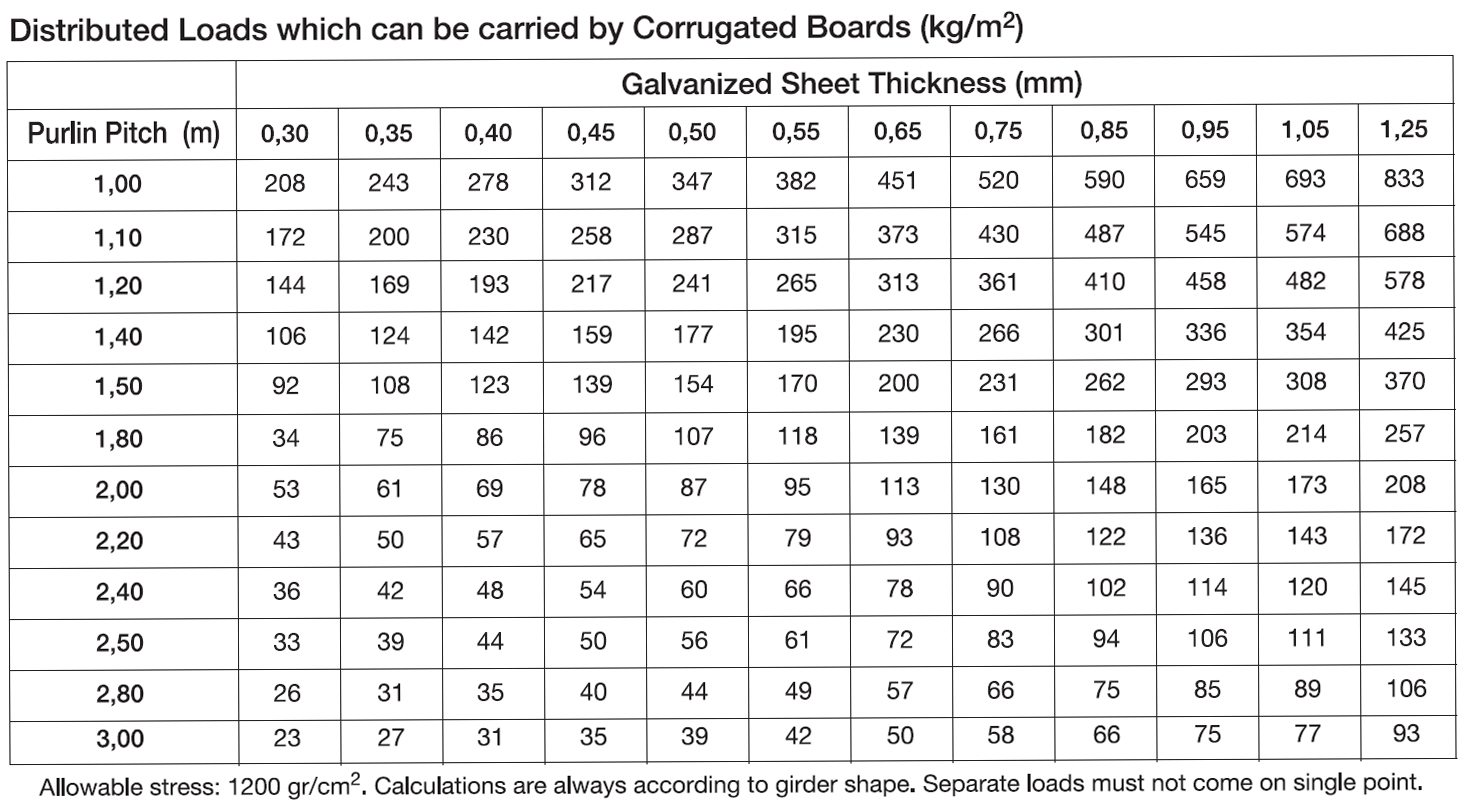
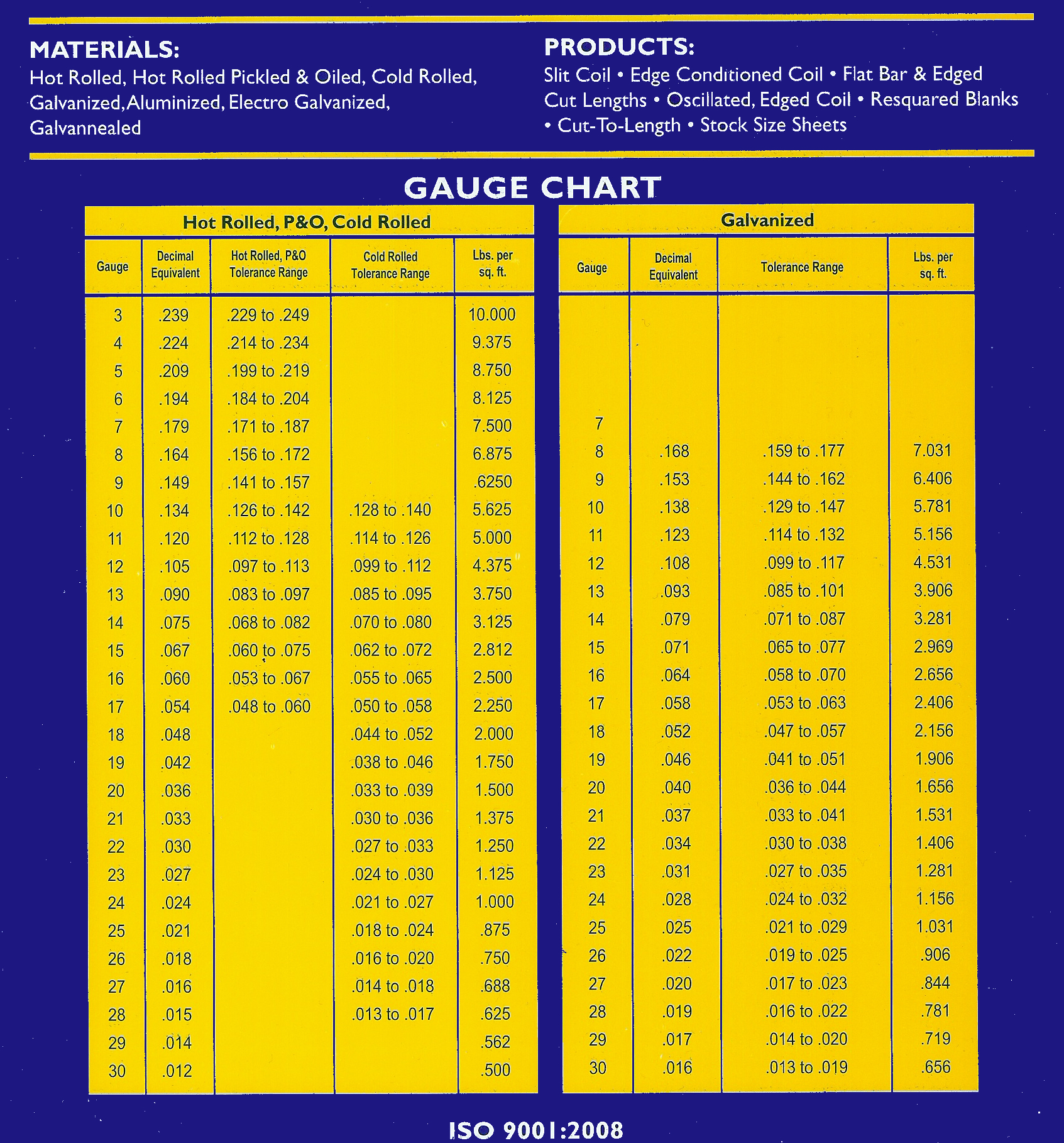
Galvanized Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
Galvanized Sheet Metal Gauge Chart - Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. The meaning of galvanize is to subject to the action of an electric current especially for the purpose of stimulating physiologically. Discover what galvanized steel is, how it’s made, and why it’s a top choice for industrial manufacturing. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. Galvanization (also spelled galvanisation) [1] is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. This zinc coating forms a protective layer to stop the steel from rusting or. The galvanized protective coating protects the iron steel substrate from. There are several galvanizing processes. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. How to use galvanize in a sentence. This zinc coating forms a protective layer to stop the steel from rusting or. Discover what galvanized steel is, how it’s made, and why it’s a top choice for industrial manufacturing. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. How to use galvanize in a sentence. Galvanized steel is standard steel that is coated in zinc to provide enhanced corrosion resistance. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. Learn about its corrosion resistance, durability, key applications, and. Galvanized steel comes in various types, developed to meet diverse applications, performance demands, and production constraints. The material due to its weight. The meaning of galvanize is to subject to the action of an electric current especially for the purpose of stimulating physiologically. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. Galvanized steel is standard steel that is coated in zinc to provide enhanced corrosion resistance. This protective technique has been a cornerstone in. Learn about its corrosion resistance, durability, key applications, and. The galvanized protective coating protects the iron steel substrate from. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. Discover what galvanized steel is, how it’s made, and why it’s a top choice for industrial manufacturing. Galvanized metal is ordinary steel covered with a protective zinc layer. How to use galvanize in a sentence. Galvanized. The meaning of galvanize is to subject to the action of an electric current especially for the purpose of stimulating physiologically. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. How to use galvanize in a sentence. Galvanization (also spelled galvanisation) [1] is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to. The material due to its weight. Galvanized steel is the main type of steel used for building purposes, i.e in structural components such as trusses, beams and columns. Discover what galvanized steel is, how it’s made, and why it’s a top choice for industrial manufacturing. There are several galvanizing processes. Galvanized steel is standard steel that is coated in zinc. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. There are several galvanizing processes. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied. Learn about its corrosion resistance, durability, key applications, and. Galvanized steel is standard steel that is coated in zinc to provide enhanced corrosion resistance. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. The material due to its weight. The galvanized protective coating protects the iron steel substrate from. Galvanized metal is ordinary steel covered with a protective zinc layer. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. The galvanized protective coating protects the iron steel. How to use galvanize in a sentence. The material due to its weight. This zinc coating forms a protective layer to stop the steel from rusting or. Galvanized steel is the main type of steel used for building purposes, i.e in structural components such as trusses, beams and columns. Discover what galvanized steel is, how it’s made, and why it’s. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. There are several galvanizing processes. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. This protective technique has been a cornerstone in. The meaning of galvanize is to. This protective technique has been a cornerstone in. Galvanization (also spelled galvanisation) [1] is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. The meaning of galvanize is to subject to the action of an electric current especially for the purpose of stimulating physiologically. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. This protective technique has been a cornerstone in. Galvanized steel is standard steel that is coated in zinc to provide enhanced corrosion resistance. This zinc coating forms a protective layer to stop the steel from rusting or. Galvanizing is a widely used industrial process designed to protect metal, particularly steel and iron, from corrosion. The meaning of galvanize is to subject to the action of an electric current especially for the purpose of stimulating physiologically. The galvanized protective coating protects the iron steel substrate from. How to use galvanize in a sentence. Galvanizing, or galvanization, is a manufacturing process where a coating of zinc is applied to steel or iron to offer protection and prevent rusting. Galvanized steel is the main type of steel used for building purposes, i.e in structural components such as trusses, beams and columns. The material due to its weight. Discover what galvanized steel is, how it’s made, and why it’s a top choice for industrial manufacturing. Galvanized steel comes in various types, developed to meet diverse applications, performance demands, and production constraints.Galvanized Sheet Metal Gauge Thickness Chart
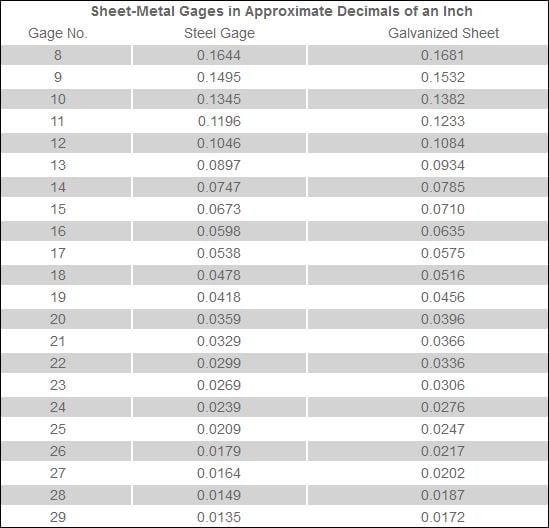
Printable Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
Galvanized Sheet Metal Gauge Thickness Chart
Galvanized Sheet Metal Gauge Thickness Chart
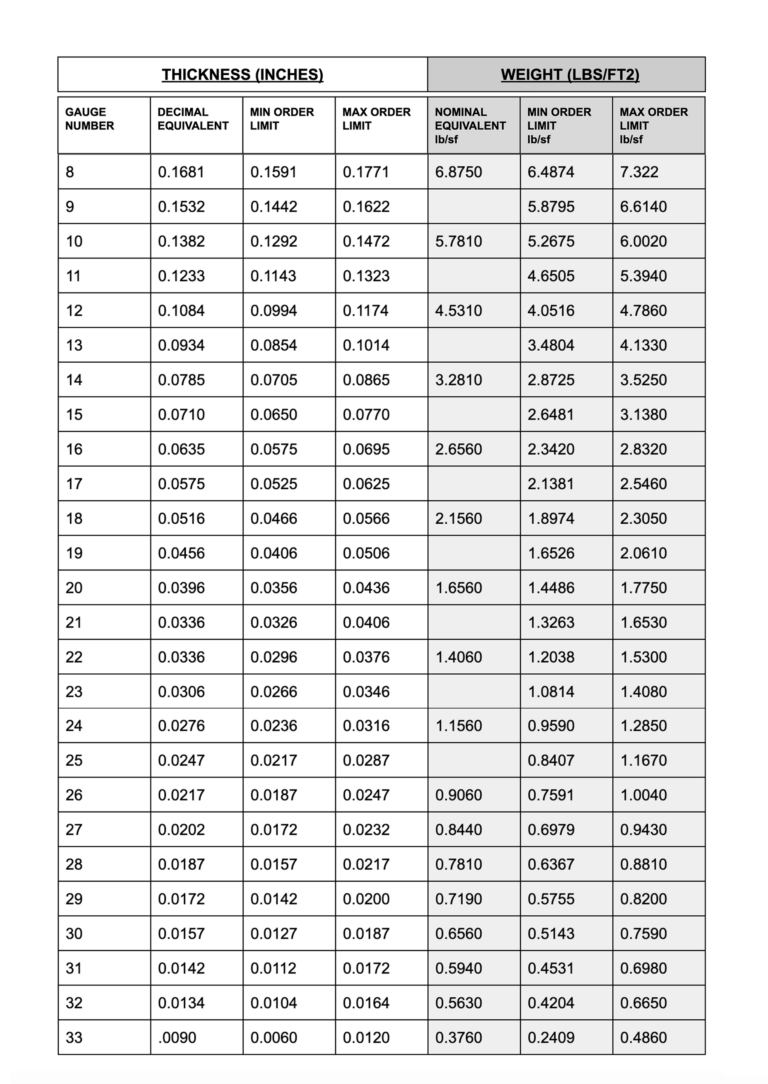
20 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal Thickness
20 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal Thickness
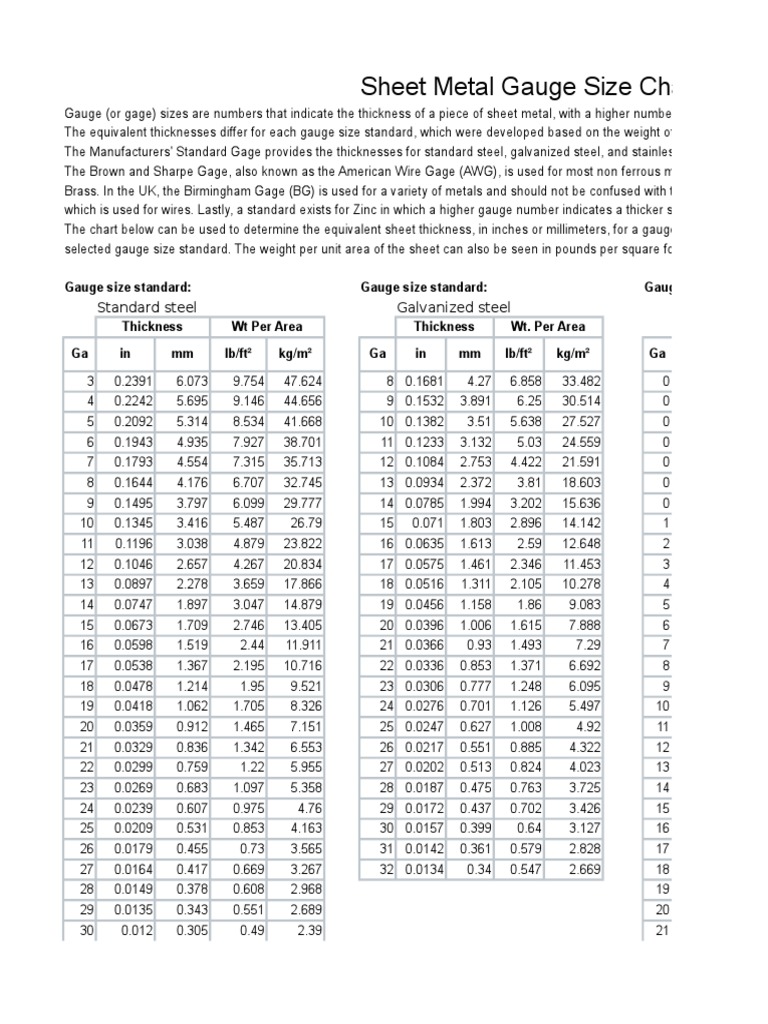
Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart Standard steel Galvanized steel
Printable Sheet Metal Gauge Chart Printable Templates
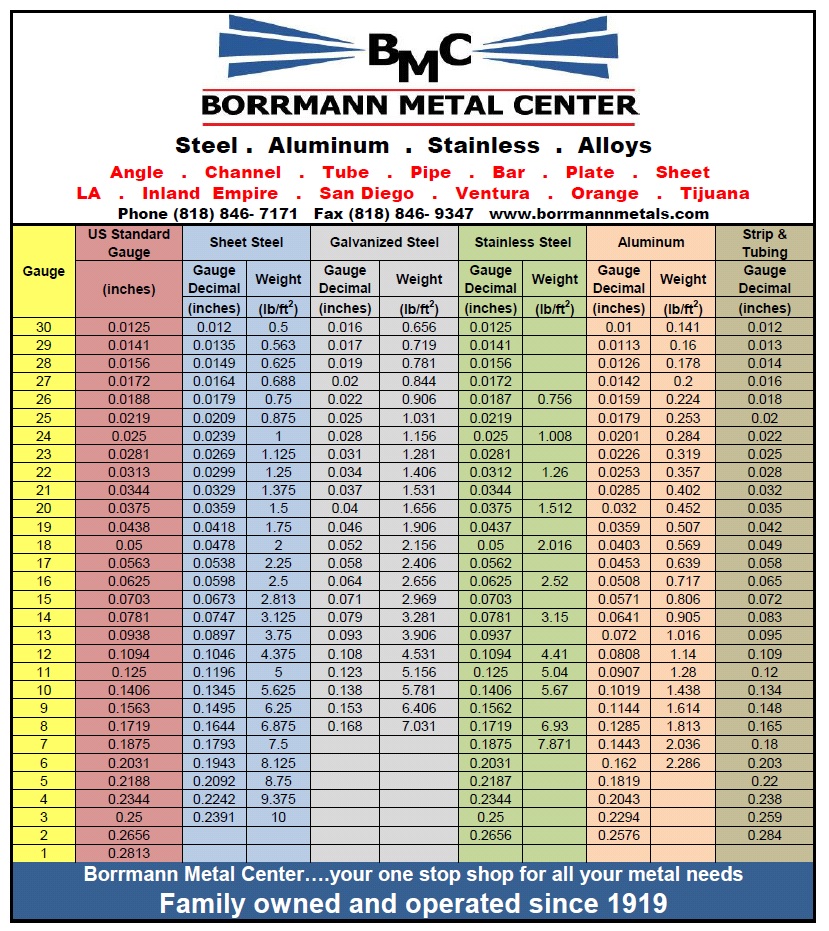
Galvanized Sheet Metal Gauge Thickness Chart
Galvanized Sheet Metal Gauge Thickness Chart
Learn About Its Corrosion Resistance, Durability, Key Applications, And.
Galvanization (Also Spelled Galvanisation) [1] Is The Process Of Applying A Protective Zinc Coating To Steel Or Iron, To Prevent Rusting.
There Are Several Galvanizing Processes.
Galvanized Metal Is Ordinary Steel Covered With A Protective Zinc Layer.
Related Post: