Fluid And Electrolyte Balance Chart
Fluid And Electrolyte Balance Chart - Fluids are a phase of matter and include liquids, gases and plasmas. A substance, as a liquid or gas, that is capable of flowing and that changes its shape at a steady rate when acted upon by a force. Most fluids are liquids or gases. A substance, as a liquid or gas, that is capable of flowing and that changes its shape at a steady rate when acted upon by a force tending to change its shape. A fluid is a liquid. A substance that flows and is not solid: The blood vessels may leak fluid, which distorts vision. In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms (flows) under an applied shear stress, or external force. The meaning of fluid is having particles that easily move and change their relative position without a separation of the mass and that easily yield to pressure : Pertaining to a substance that easily changes its. Fluid (countable and uncountable, plural fluids) any substance which can flow with relative ease, tends to assume the shape of its container, and obeys bernoulli's principle; They have zero shear modulus, or, in. In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. Fluid movements or lines or designs are smooth and graceful. Fluids are a phase of matter and include liquids, gases and plasmas. A continuous, amorphous substance whose molecules move freely past one another and that has the tendency to assume the shape of its container; A fluid is a material that flows or continuously deforms under a shear (tangential stress). Examples include air and water. Most fluids are liquids or gases. A fluid is a material that flows or continuously deforms under a shear (tangential stress). The blood vessels may leak fluid, which distorts vision. A continuous, amorphous substance whose molecules move freely past one another and that has the tendency to assume the shape of its container; A substance, as a liquid or gas, that is capable of flowing and. In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. Most fluids are liquids or gases. Fluid (countable and uncountable, plural fluids) any substance which can flow with relative ease, tends to assume the shape of its container, and obeys bernoulli's principle; Make sure. A fluid is a liquid. A substance that flows and is not solid: In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. Most fluids are liquids or gases. The blood vessels may leak fluid, which distorts vision. Pertaining to a substance that easily changes its. The blood vessels may leak fluid, which distorts vision. In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in. Fluids are a phase of matter and include liquids, gases. Fluid movements or lines or designs are smooth and graceful. Fluids are a phase of matter and include liquids, gases and plasmas. Most fluids are liquids or gases. A substance, as a liquid or gas, that is capable of flowing and that changes its shape at a steady rate when acted upon by a force. In physics, a fluid is. Pertaining to a substance that easily changes its. In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. The blood vessels may leak fluid, which distorts vision. Fluid movements or lines or designs are smooth and graceful. A substance, as a liquid or gas,. A substance that flows and is not solid: A substance, as a liquid or gas, that is capable of flowing and that changes its shape at a steady rate when acted upon by a force. A fluid is a liquid. In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms (flows) under an applied shear stress, or external force. A. Examples include air and water. A substance that flows and is not solid: Pertaining to a substance that easily changes its. Most fluids are liquids or gases. The meaning of fluid is having particles that easily move and change their relative position without a separation of the mass and that easily yield to pressure : In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. A continuous, amorphous substance whose molecules move freely past one another and that has the tendency to assume the shape of its container; Examples include air and water. Make sure that you drink plenty. The blood vessels may leak fluid, which distorts vision. In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in. Examples include air and water. Pertaining to a substance that easily changes its. A substance, as a liquid or gas, that is capable of flowing and that changes its shape at a steady rate when acted upon by a force tending to change its shape. Most fluids are liquids or gases. They have zero shear modulus, or, in. Pertaining to a substance that easily changes its. A continuous, amorphous substance whose molecules move freely past one another and that has the tendency to assume the shape of its container; A substance, as a liquid or gas, that is capable of flowing and that changes its shape at a steady rate when acted upon by a force. Fluids are a phase of matter and include liquids, gases and plasmas. The meaning of fluid is having particles that easily move and change their relative position without a separation of the mass and that easily yield to pressure : A fluid is a liquid. A fluid is a material that flows or continuously deforms under a shear (tangential stress). In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms (flows) under an applied shear stress, or external force. Fluid (countable and uncountable, plural fluids) any substance which can flow with relative ease, tends to assume the shape of its container, and obeys bernoulli's principle; Examples include air and water. In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force.Fluid & Electrolytes Cheat Sheet HYPERkalemia (over 3) Heart TIGHT & CONTRACTED 1 ST Studocu
Electrolyte Chart For Nursing
Fluid And Electrolytes Practice Questions
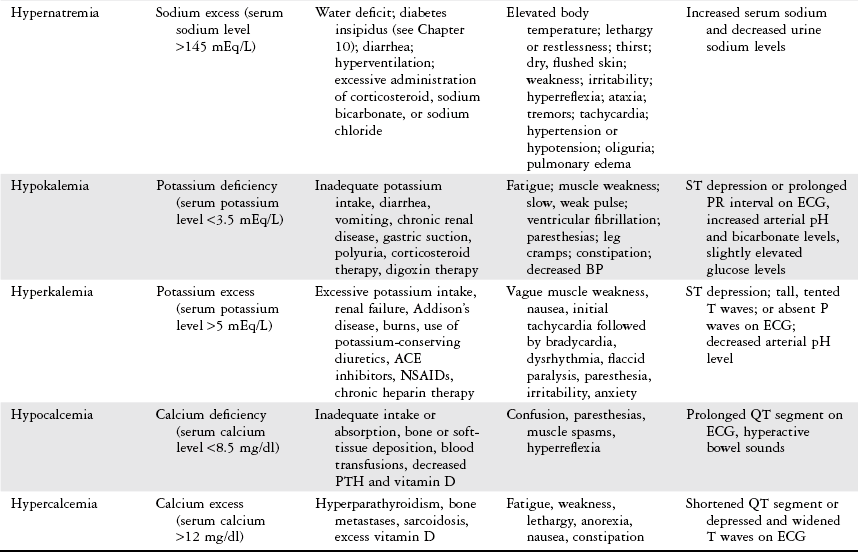
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance Chart Fluid/Electrolyte Imbalance Causes Signs/Symptoms Lab
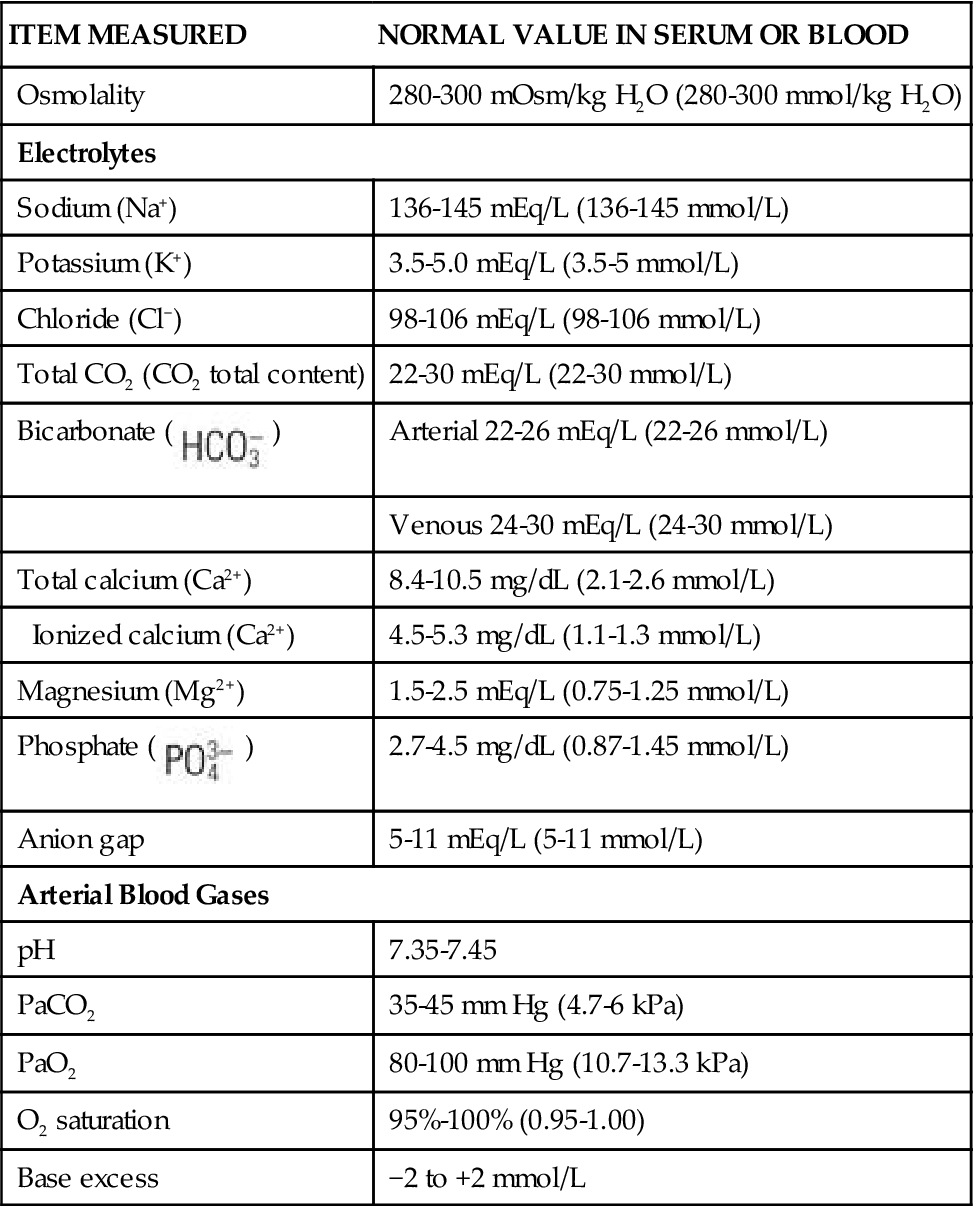
Fluid And Electrolytes Notes Pdf
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Musculoskeletal Key
PPT Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolytes, and Acid/Base Balance Lecture 17 PowerPoint Presentation
Electrolyte Balance Chart
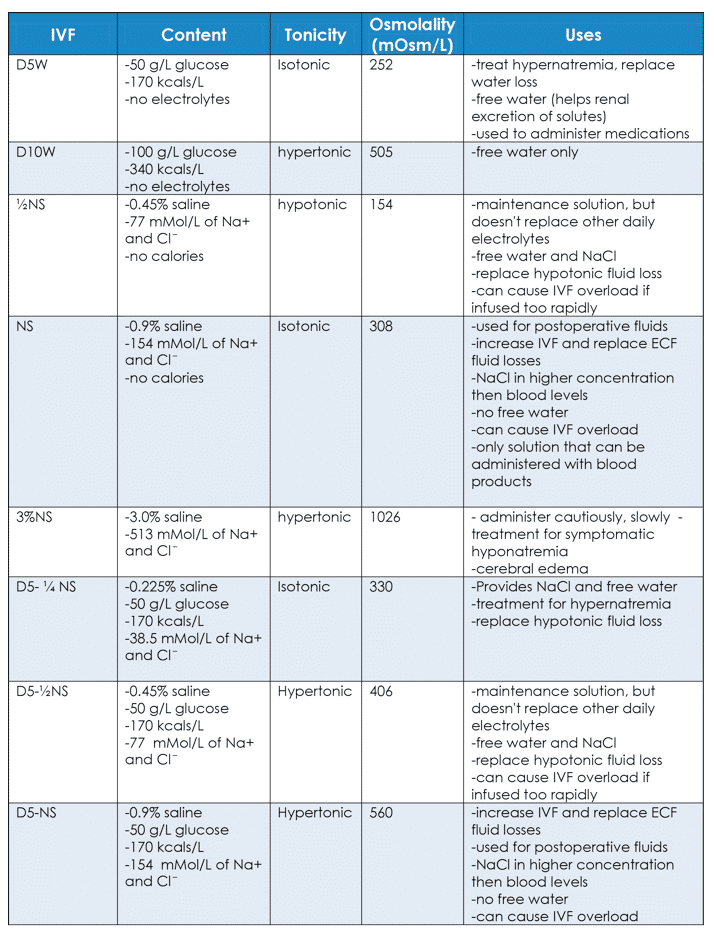
Fluid and Electrolytes Study Guide for Nurses
Fluid, Electrolyte, and AcidBase Balance Nurse Key
The Blood Vessels May Leak Fluid, Which Distorts Vision.
A Substance That Flows And Is Not Solid:
Fluid Movements Or Lines Or Designs Are Smooth And Graceful.
Make Sure That You Drink Plenty Of Fluids.
Related Post: