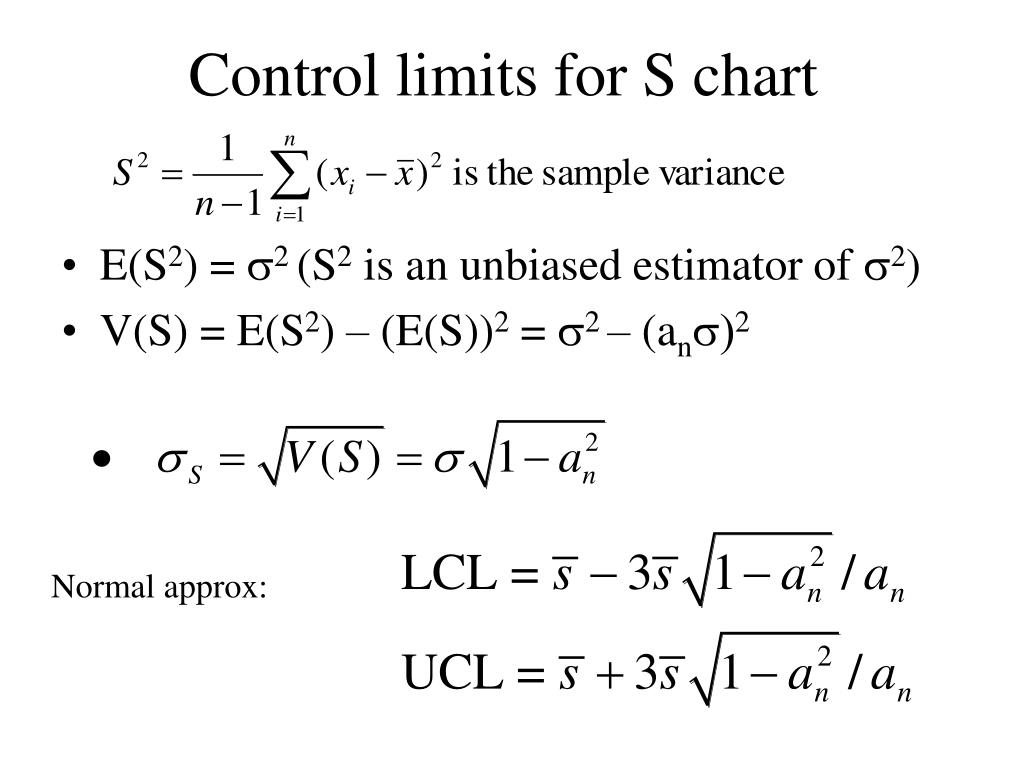
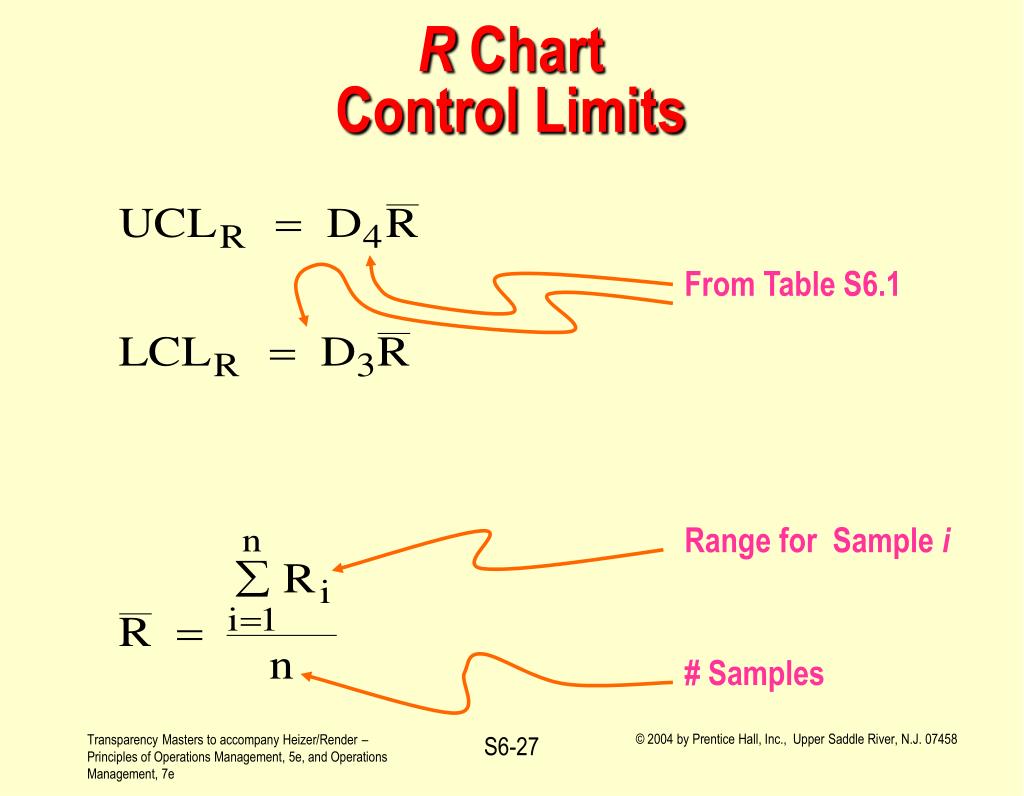
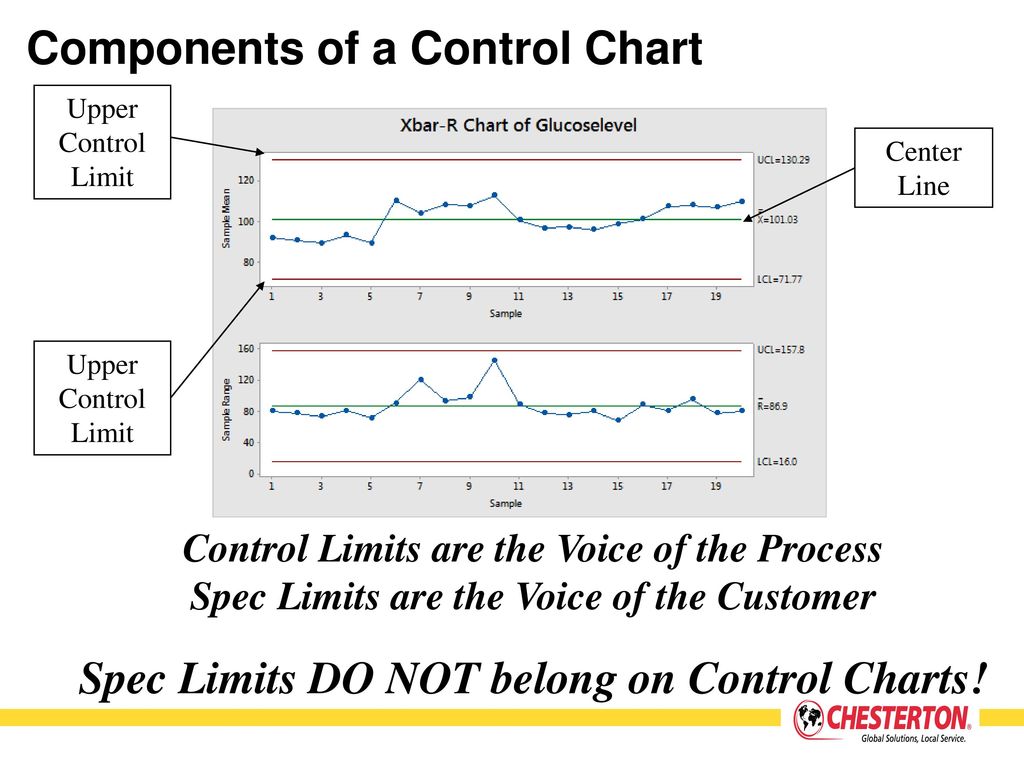
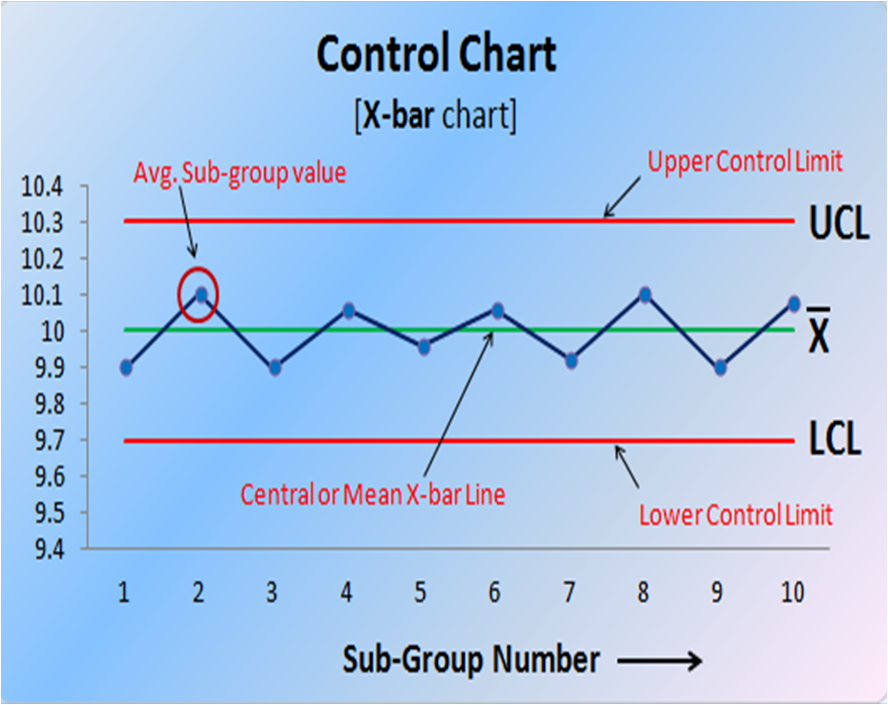
Control Chart Limits
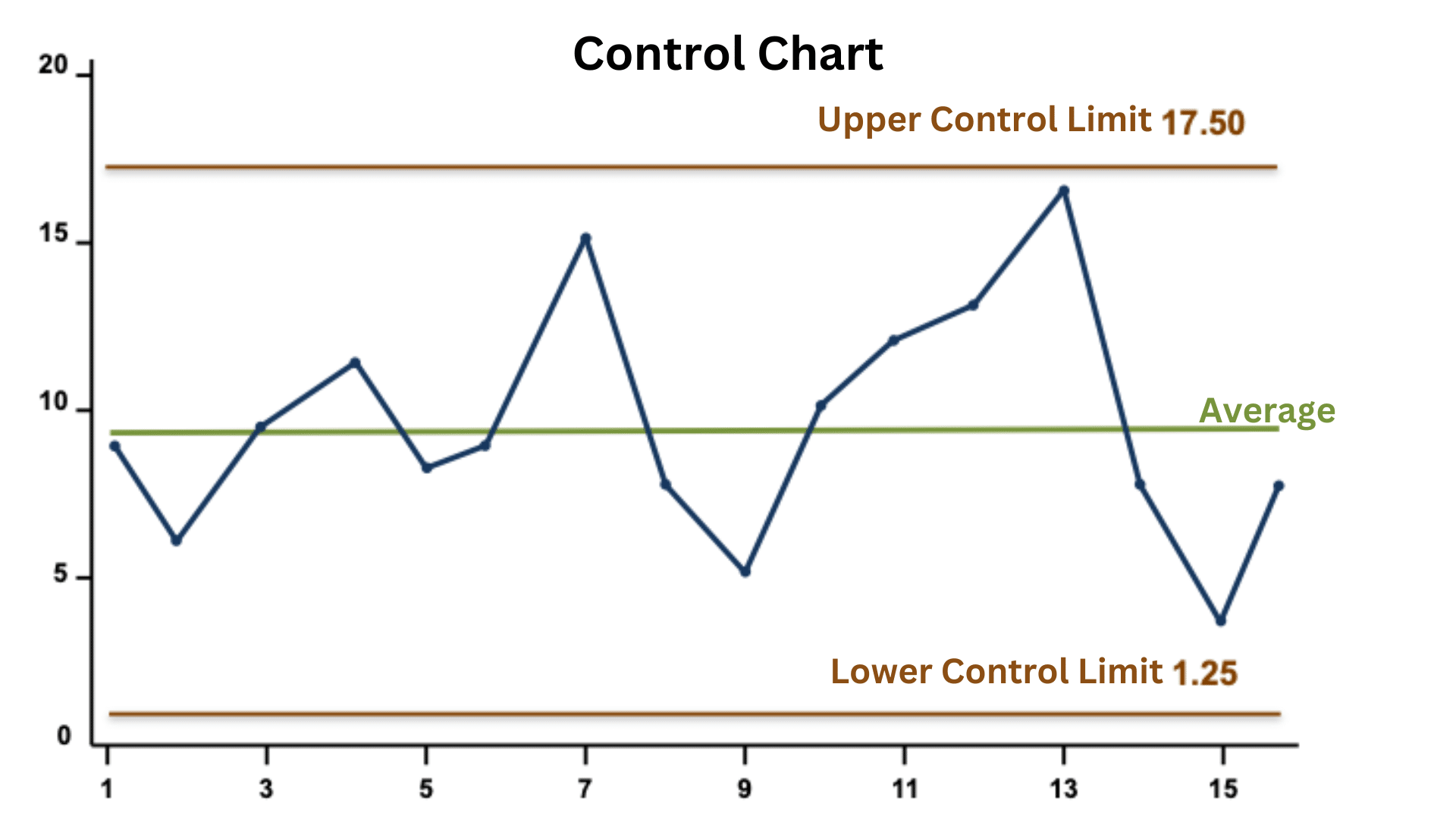
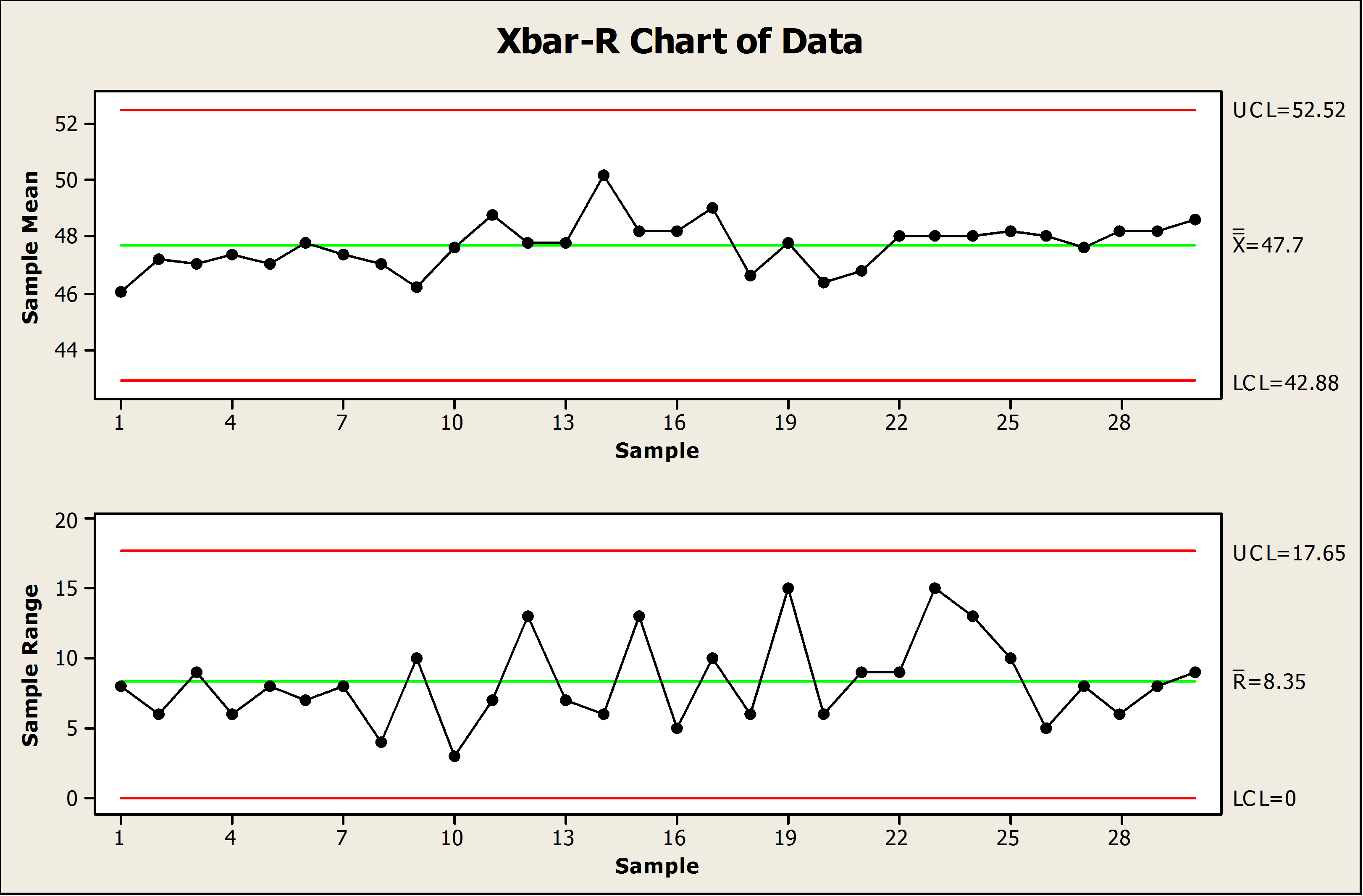
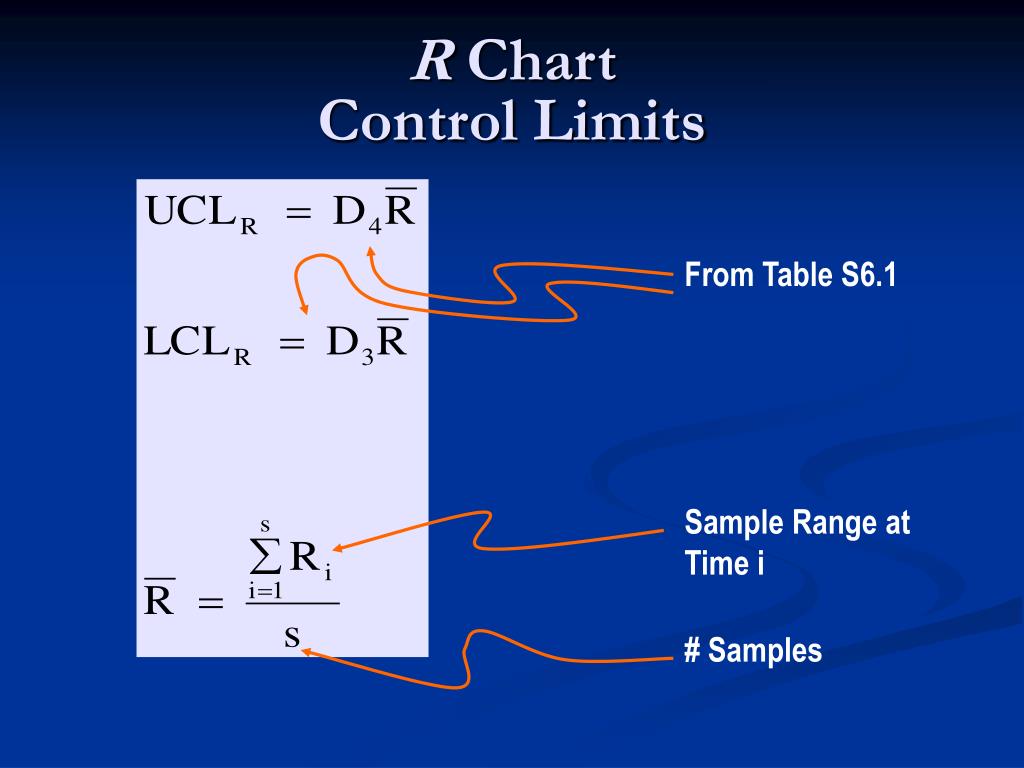
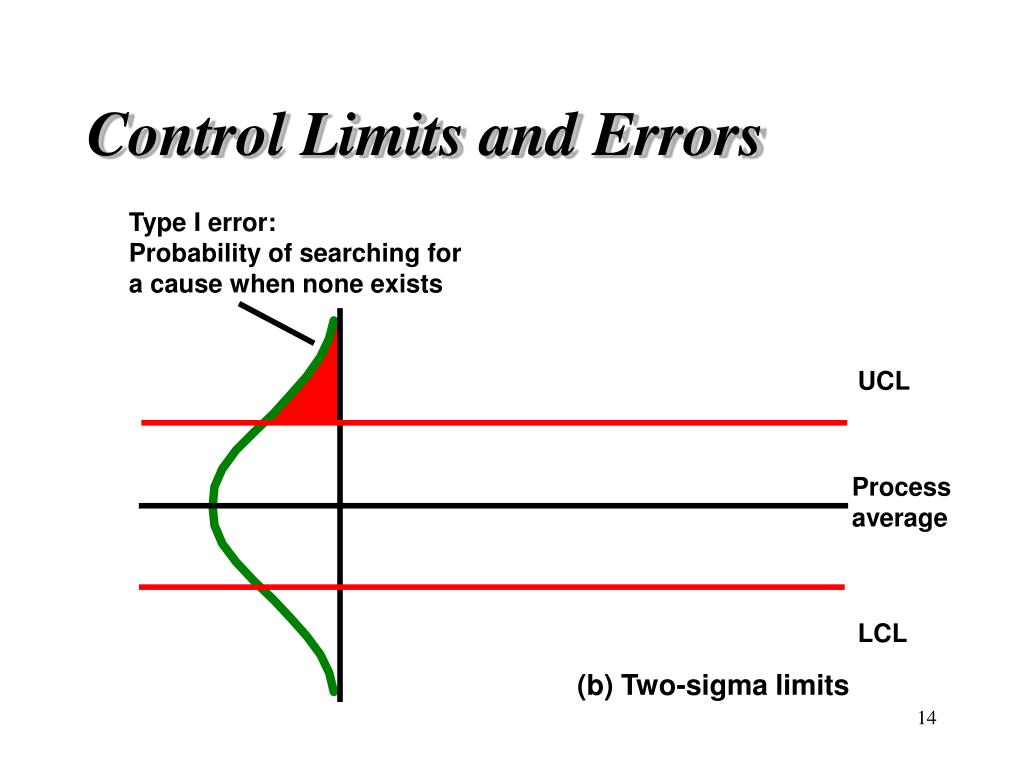
Control Chart Limits - When you have at least 20 sequential. This is the maximum value a data point can reach before it indicates that the process might be going out of control. Early detection prevents tampering, sustains six sigma stability, and. It is usually set at 3 standard. Control charts are graphical representations of process data over time. One is the upper control limit (ucl). Two other horizontal lines, called the upper control limit (ucl) and the lower control. Control limits distinguish control charts from a simple line graph or run chart. They are like traffic lanes that help you determine if your process is stable and predicable or not. They show whether the manufacturing process is stable and operating within expected parameters. If so, the control limits calculated from the first 20 points are conditional limits. This is the maximum value a data point can reach before it indicates that the process might be going out of control. When you start a new control chart, the process may be out of control. Once you have enough data, you calculate the average and the control limits. They show whether the manufacturing process is stable and operating within expected parameters. It is usually set at 3 standard. Control charts are graphical representations of process data over time. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into control charts, their components, types, how to define control limits, and the rules for determining whether a process is out of control. There are usually two control limits. Control limits are the voice of the process (different from specification limits, which are the voice of the customer.) they show what the process is doing and act as a guide for. There are usually two control limits. This is the largest value you would. Once you have enough data, you calculate the average and the control limits. They are like traffic lanes that help you determine if your process is stable and predicable or not. Two other horizontal lines, called the upper control limit (ucl) and the lower control. Control charts are graphical representations of process data over time. Control limits are the voice of the process (different from specification limits, which are the voice of the customer.) they show what the process is doing and act as a guide for. This is the largest value you would. They show whether the manufacturing process is stable and operating within. They show whether the manufacturing process is stable and operating within expected parameters. Two other horizontal lines, called the upper control limit (ucl) and the lower control. Control limits distinguish control charts from a simple line graph or run chart. When you start a new control chart, the process may be out of control. This is the largest value you. They show whether the manufacturing process is stable and operating within expected parameters. This is the largest value you would. One is the upper control limit (ucl). There are usually two control limits. A control chart begins with a time series graph. If so, the control limits calculated from the first 20 points are conditional limits. Two other horizontal lines, called the upper control limit (ucl) and the lower control. A control chart begins with a time series graph. When you have at least 20 sequential. They show whether the manufacturing process is stable and operating within expected parameters. One is the upper control limit (ucl). Once you have enough data, you calculate the average and the control limits. This is the largest value you would. If so, the control limits calculated from the first 20 points are conditional limits. Two other horizontal lines, called the upper control limit (ucl) and the lower control. This is the maximum value a data point can reach before it indicates that the process might be going out of control. Control limits distinguish control charts from a simple line graph or run chart. There are usually two control limits. Two other horizontal lines, called the upper control limit (ucl) and the lower control. They show whether the manufacturing. A control chart begins with a time series graph. One is the upper control limit (ucl). It is usually set at 3 standard. This is the largest value you would. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into control charts, their components, types, how to define control limits, and the rules for determining whether a process is out of. This is the largest value you would. There are usually two control limits. Control charts are graphical representations of process data over time. Control limits are the voice of the process (different from specification limits, which are the voice of the customer.) they show what the process is doing and act as a guide for. If so, the control limits. Once you have enough data, you calculate the average and the control limits. Control limits distinguish control charts from a simple line graph or run chart. It is usually set at 3 standard. Control limits are the voice of the process (different from specification limits, which are the voice of the customer.) they show what the process is doing and. They show whether the manufacturing process is stable and operating within expected parameters. When you start a new control chart, the process may be out of control. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into control charts, their components, types, how to define control limits, and the rules for determining whether a process is out of control. One is the upper control limit (ucl). Control limits are the voice of the process (different from specification limits, which are the voice of the customer.) they show what the process is doing and act as a guide for. They are like traffic lanes that help you determine if your process is stable and predicable or not. A control chart begins with a time series graph. When you have at least 20 sequential. This is the maximum value a data point can reach before it indicates that the process might be going out of control. Control charts are graphical representations of process data over time. If so, the control limits calculated from the first 20 points are conditional limits. Once you have enough data, you calculate the average and the control limits. Control limits distinguish control charts from a simple line graph or run chart. Two other horizontal lines, called the upper control limit (ucl) and the lower control.A Beginner's Guide to Control Charts The W. Edwards Deming Institute
Statistical Process Control PresentationEZE
Control Chart Diagram Example Control Chart Process Statisti
PPT Statistical Process Control PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID634041
PPT CHAPTER 5 VARIABLE CONTROL CHARTS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6621759
PPT Statistical Process Control PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5392306
Qc Quality Control Tools Are Basic Statistical Process Control Spc
PPT Operations Management Statistical Process Control Supplement 6 PowerPoint Presentation
SPC Statistical Process Control ppt download
What is Control Chart ? SPC Chart Shewhart Chart
There Are Usually Two Control Limits.
Early Detection Prevents Tampering, Sustains Six Sigma Stability, And.
This Is The Largest Value You Would.
It Is Usually Set At 3 Standard.
Related Post: