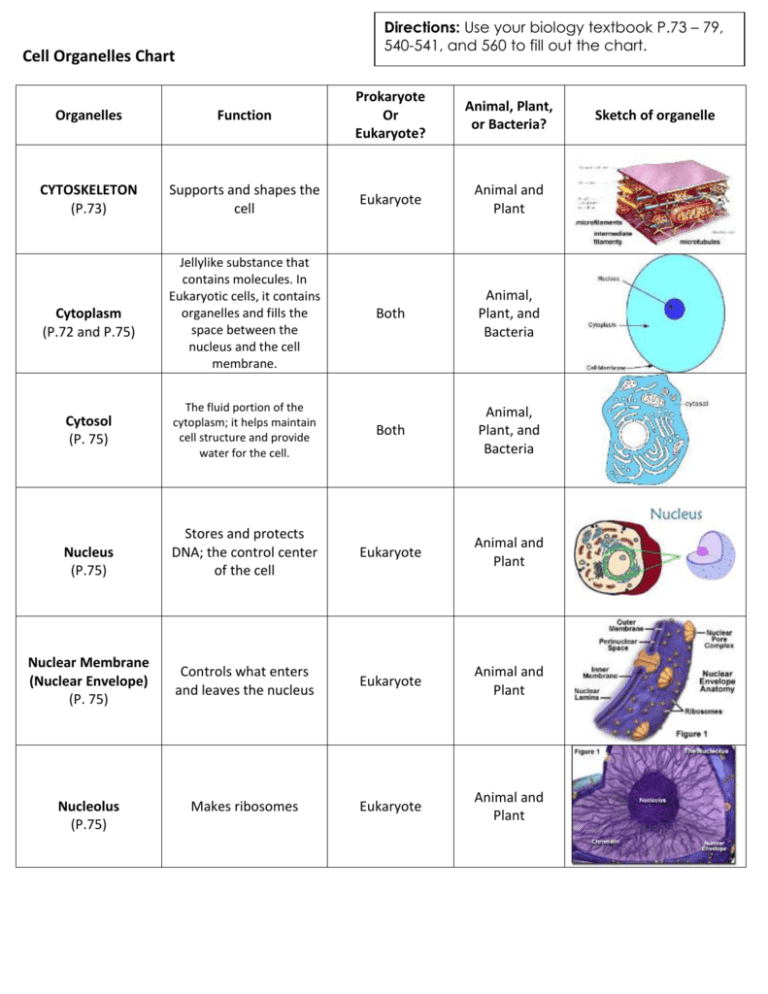
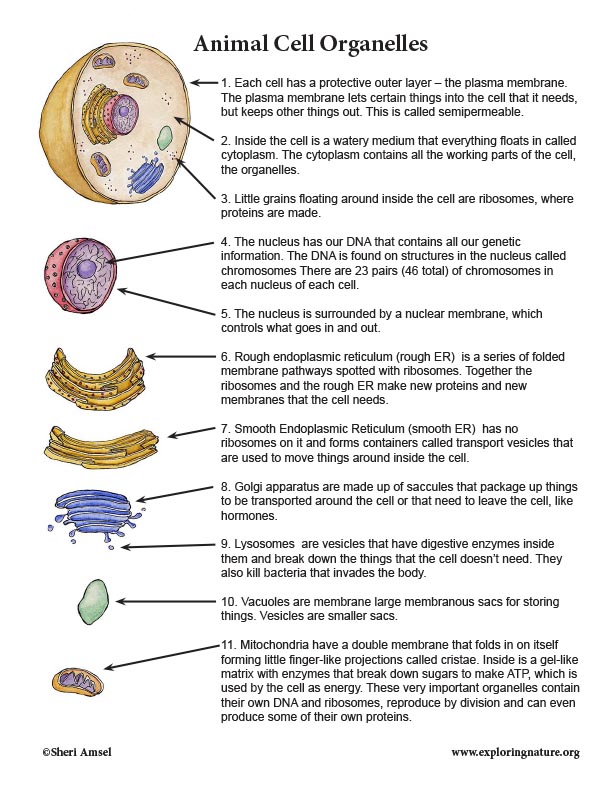
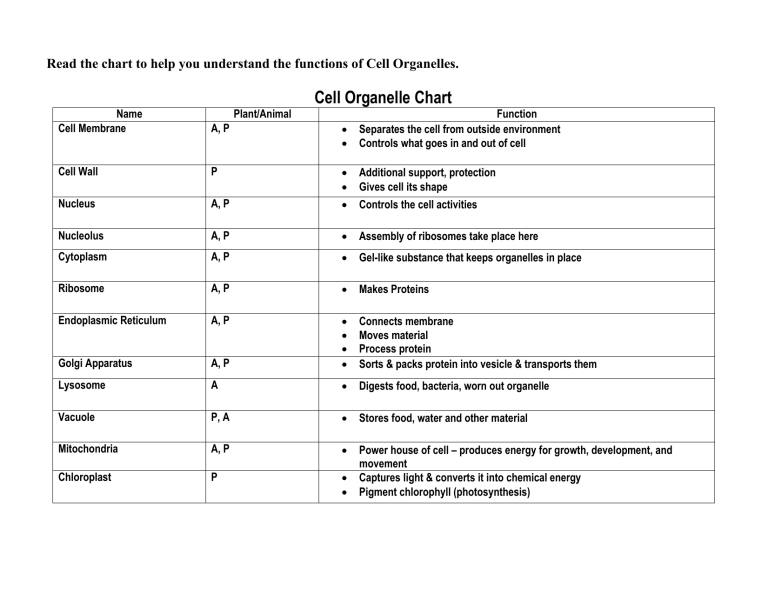
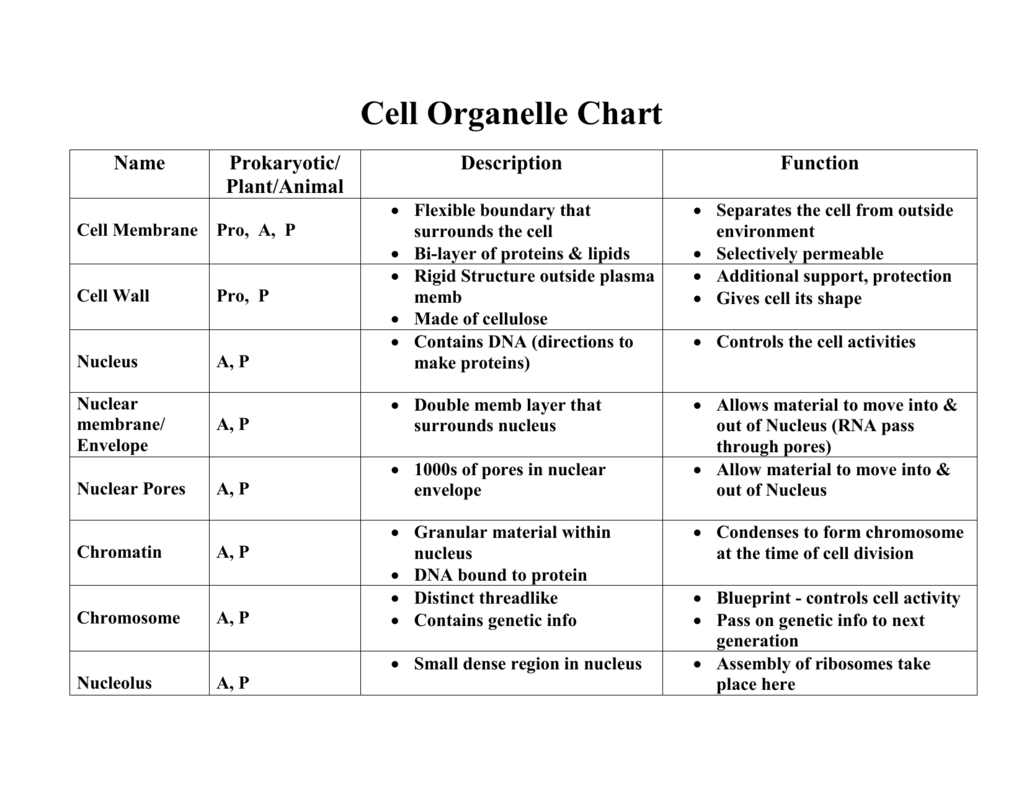
Cell Organelle Chart
Cell Organelle Chart - Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. A single cell is often a complete. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. Inside every cell is a host of structures known as organelles. “every cell has essential structures that are the same, like every house has a. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. A cell is the smallest living unit. Inside every cell is a host of structures known as organelles. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. A single cell is often a complete. “every cell has essential structures that are the same, like every house has a. Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and. “every cell has essential structures that are the same, like every house has a. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. A single cell is often a complete. A cell is the smallest living unit. Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology,. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. A cell is the smallest living unit. Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular. “every cell has essential structures that are the same, like every house has a. Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and. A cell is the smallest living unit. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. A cell is the smallest living unit. “every cell has essential structures that are the same, like every house has a. Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience,. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. “every cell has essential structures that are the same, like every house has a. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. Inside every cell is a host of structures known as organelles. Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and. “every cell has essential. A cell is the smallest living unit. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. Inside every cell is a host of structures known as organelles. A cell is the smallest living unit. A single cell is often a complete. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Cell cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. A cell is the smallest living unit. Cells emerged. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. A cell is the smallest living unit. Together, trillions of cells make up the human body. Inside every cell is a host of structures known as organelles. Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. “every cell has essential structures that are the same, like every house has a. Cells are broadly categorized into two types:Cell Organelles Chart Functions & Cell Types
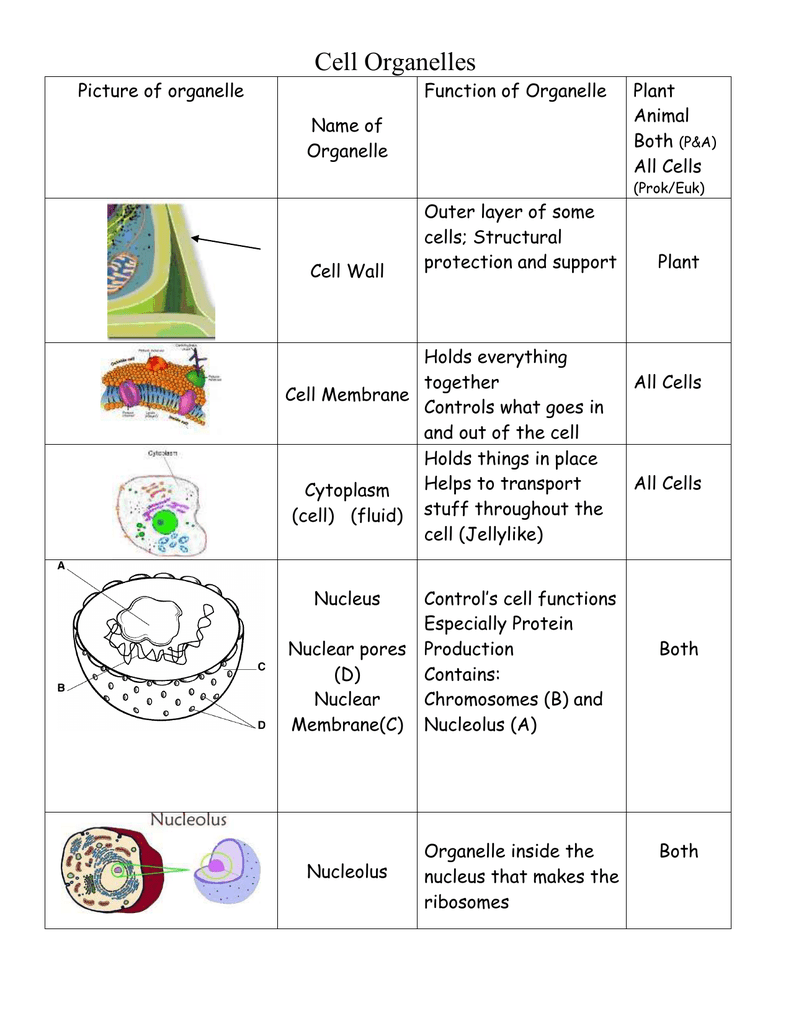
Cell Organelles
Unit 2 Cells & Organelles Mr Plowman
Cell Organelle Chart Functions & Types
Cell Organelle Chart
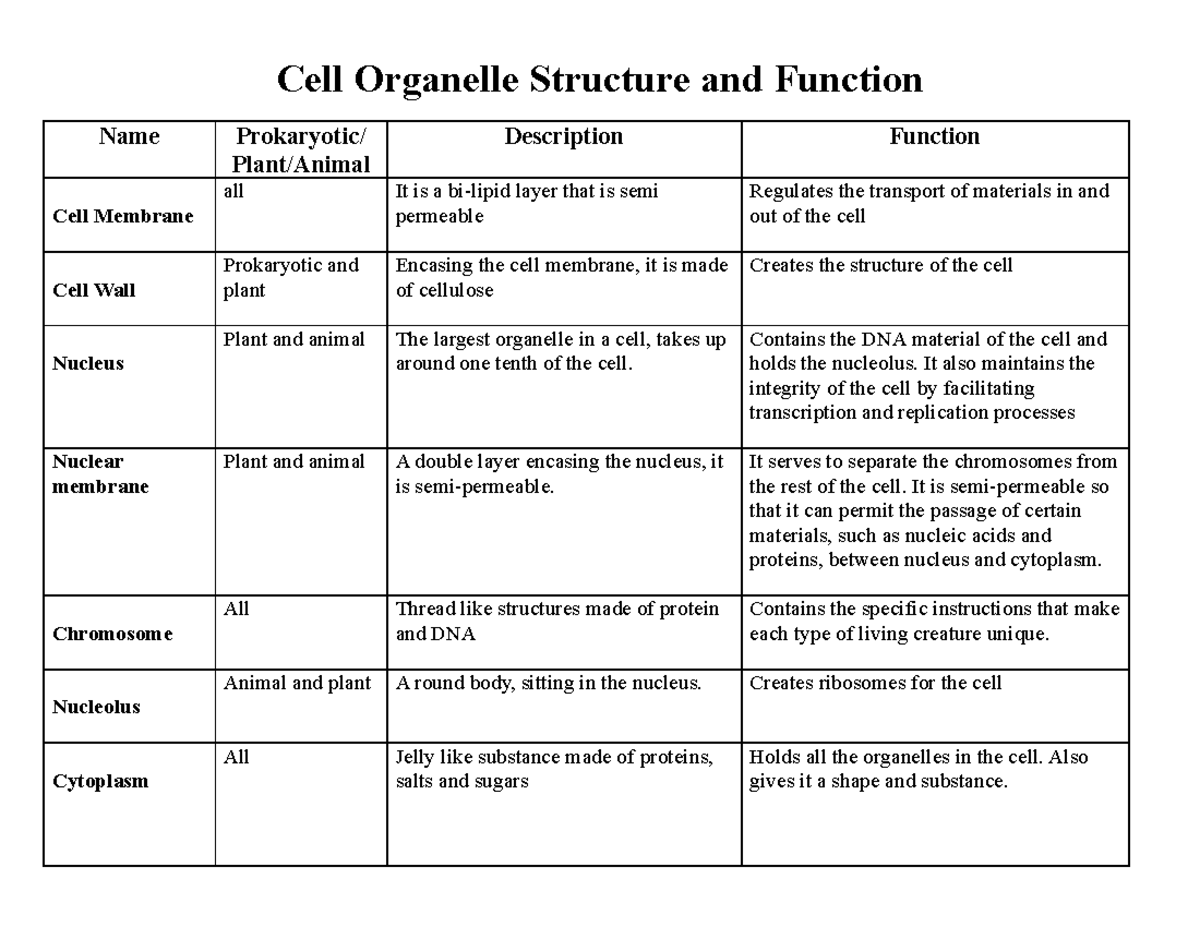
Cell Organelle Table biology mod 1 year 11 Cell Organelle Structure and Function Name
Cell Organelle
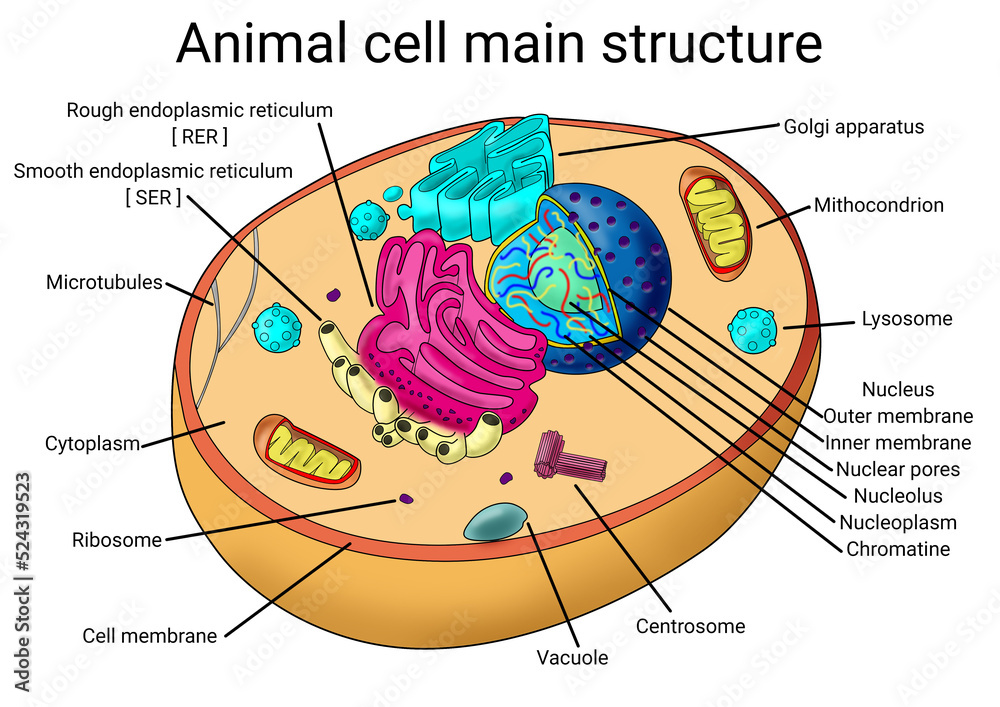
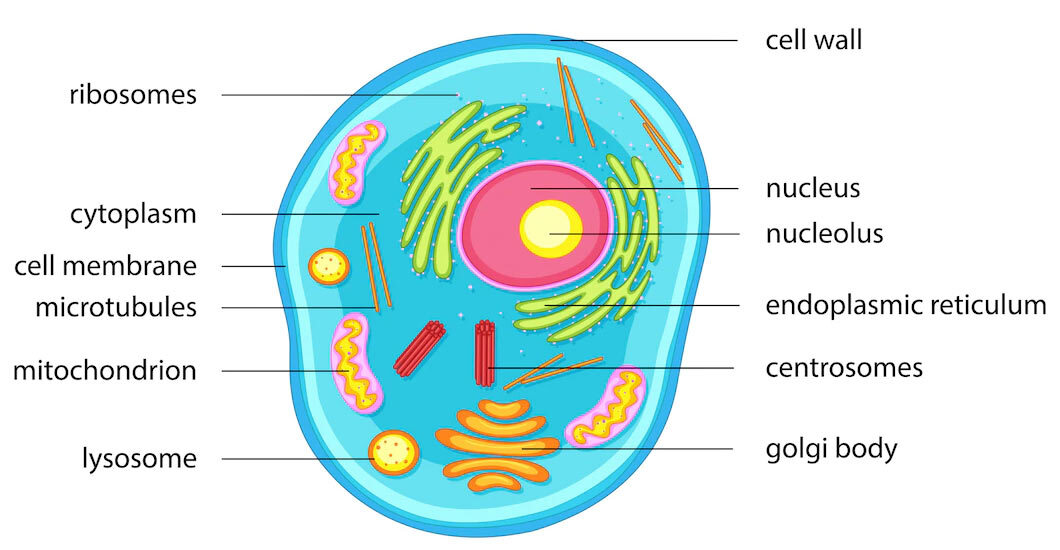
Printable chart Science Cytology biology animal cell structure diagram school medicine medical
Cell Organelle — Types & Functions Expii
Cell Organelles Definition, Structure, Types, Functions
A Cell Is The Smallest Living Organism And The Basic Unit Of Life On Earth.
Cell Cell Publishes Findings Of Unusual Significance In Any Area Of Experimental Biology, Including But Not Limited To Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Neuroscience, Immunology, Virology And.
A Single Cell Is Often A Complete.
Related Post: