Calibration Chart Chart Industries
Calibration Chart Chart Industries - It ensures that the instrument. At its core, calibration is the process of comparing the performance of a measurement device (such as a thermometer, scale, or pressure gauge) against a recognized. A person typically performs a calibration to determine. In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Learn about the meaning of calibration, calibration uncertainty, traceability, why and how often to calibrate and how to calibrate. To calibrate testing equipment is to level gear so measurements remain accurate and consistent. Calibration keeps results honest and trustworthy, which counts Calibration is the act of comparing a device under test (dut) of an unknown value with a reference standard of a known value. Learn how it mitigates risks, reduces costs, and ensures compliance. Calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of a measuring instrument or system, such as an electronic device or sensor, to ensure that it provides the. At its core, calibration is the process of comparing the performance of a measurement device (such as a thermometer, scale, or pressure gauge) against a recognized. It ensures that the instrument. Discover the critical role of calibration in industrial manufacturing. Calibration is the act of comparing a device under test (dut) of an unknown value with a reference standard of a known value. Learn about the meaning of calibration, calibration uncertainty, traceability, why and how often to calibrate and how to calibrate. Calibration keeps results honest and trustworthy, which counts Calibration is the process of comparing the readings of a measuring instrument with a known standard value and making adjustments if needed. A person typically performs a calibration to determine. Learn how it mitigates risks, reduces costs, and ensures compliance. In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. To calibrate testing equipment is to level gear so measurements remain accurate and consistent. Learn about the meaning of calibration, calibration uncertainty, traceability, why and how often to calibrate and how to calibrate. Calibration is the process of comparing the readings of a measuring instrument with a known standard value and making adjustments if needed. Discover the critical role of. Learn how it mitigates risks, reduces costs, and ensures compliance. The process of comparison of a device with unknown accuracy to a device with a known, accurate standard to eliminate any variation in the device being checked is called calibration. To calibrate testing equipment is to level gear so measurements remain accurate and consistent. Discover the critical role of calibration. Discover the critical role of calibration in industrial manufacturing. Calibration is the process of comparing the readings of a measuring instrument with a known standard value and making adjustments if needed. Calibration keeps results honest and trustworthy, which counts It ensures that the instrument. In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device. Learn how it mitigates risks, reduces costs, and ensures compliance. Calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of a measuring instrument or system, such as an electronic device or sensor, to ensure that it provides the. It ensures that the instrument. The process of comparison of a device with unknown accuracy to a device with a known,. At its core, calibration is the process of comparing the performance of a measurement device (such as a thermometer, scale, or pressure gauge) against a recognized. Calibration is the process of comparing the readings of a measuring instrument with a known standard value and making adjustments if needed. Learn how it mitigates risks, reduces costs, and ensures compliance. Discover the. To calibrate testing equipment is to level gear so measurements remain accurate and consistent. Learn how it mitigates risks, reduces costs, and ensures compliance. In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Discover the critical role of calibration in industrial manufacturing.. Calibration is the process of comparing the readings of a measuring instrument with a known standard value and making adjustments if needed. It ensures that the instrument. The process of comparison of a device with unknown accuracy to a device with a known, accurate standard to eliminate any variation in the device being checked is called calibration. At its core,. Calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of a measuring instrument or system, such as an electronic device or sensor, to ensure that it provides the. A person typically performs a calibration to determine. The process of comparison of a device with unknown accuracy to a device with a known, accurate standard to eliminate any variation in. In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. A person typically performs a calibration to determine. Learn about the meaning of calibration, calibration uncertainty, traceability, why and how often to calibrate and how to calibrate. Calibration is the process of comparing. Calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of a measuring instrument or system, such as an electronic device or sensor, to ensure that it provides the. Learn about the meaning of calibration, calibration uncertainty, traceability, why and how often to calibrate and how to calibrate. Calibration is the process of comparing the readings of a measuring instrument. Calibration is the act of comparing a device under test (dut) of an unknown value with a reference standard of a known value. At its core, calibration is the process of comparing the performance of a measurement device (such as a thermometer, scale, or pressure gauge) against a recognized. Calibration keeps results honest and trustworthy, which counts Discover the critical role of calibration in industrial manufacturing. To calibrate testing equipment is to level gear so measurements remain accurate and consistent. Calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of a measuring instrument or system, such as an electronic device or sensor, to ensure that it provides the. Learn about the meaning of calibration, calibration uncertainty, traceability, why and how often to calibrate and how to calibrate. In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Calibration is the process of comparing the readings of a measuring instrument with a known standard value and making adjustments if needed. Learn how it mitigates risks, reduces costs, and ensures compliance.Scale Calibration Log Sheet
Tank Calibration Charts AfrisoEurogauge
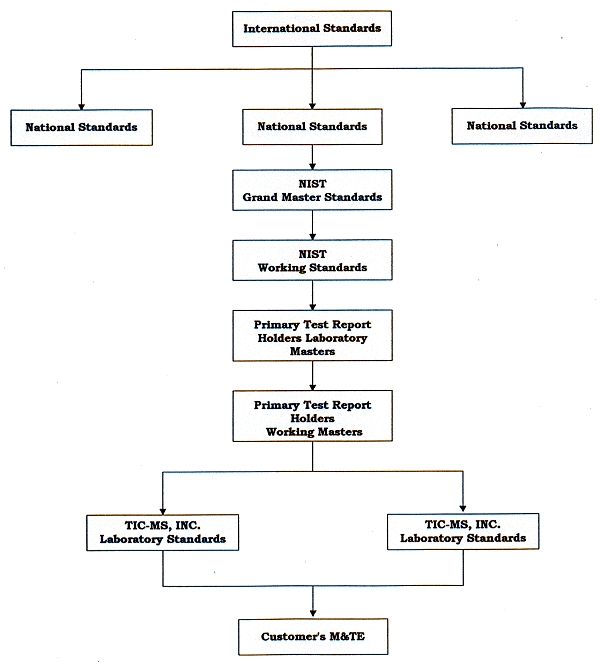
Calibration Traceability Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Calibration Chart Calibration Chart Calibration Chart Calibration Chart PDF
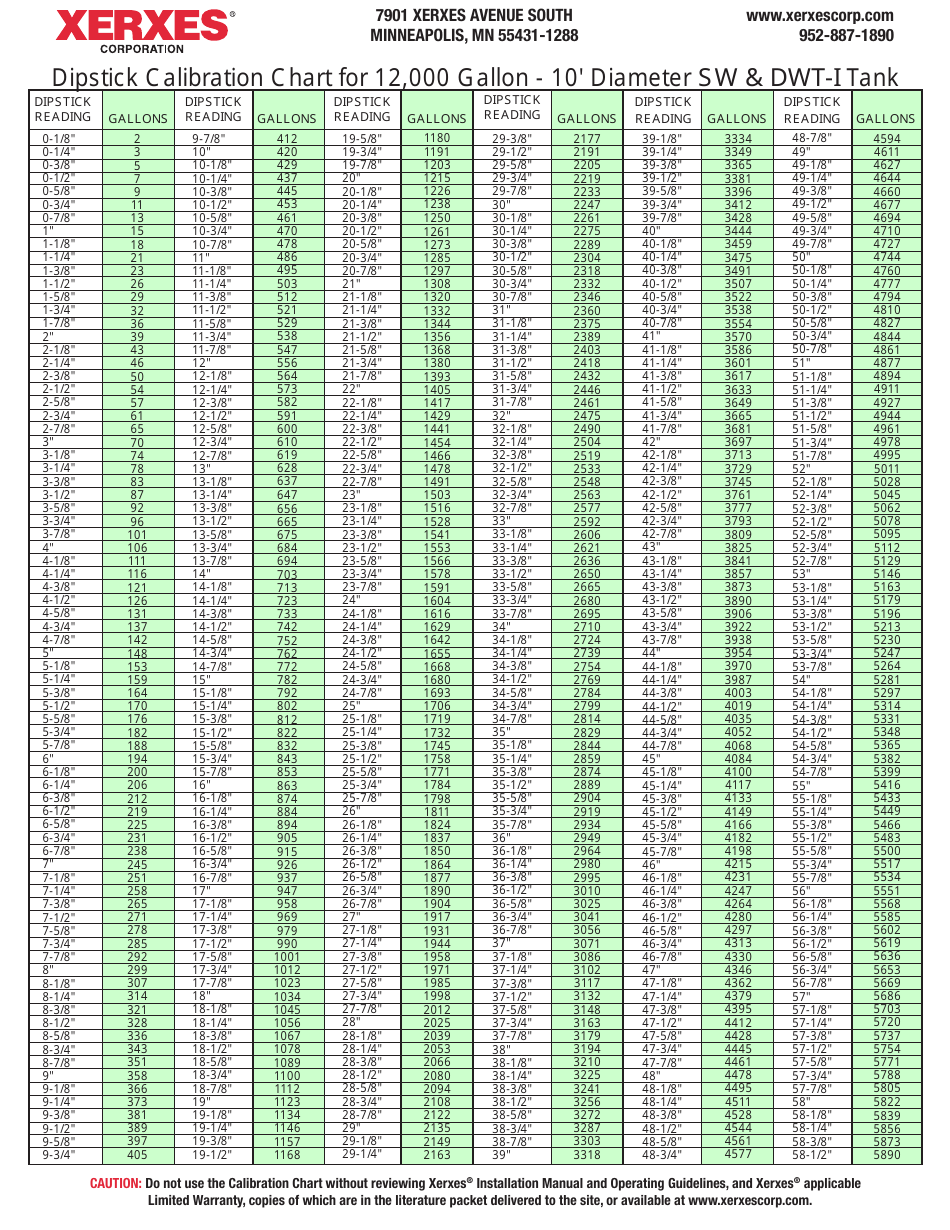
Dipstick Calibration Chart Xerxes Corporation Download Printable PDF Templateroller
Calibration Chart Format PDF Nature
Calibration chart. Download Scientific Diagram
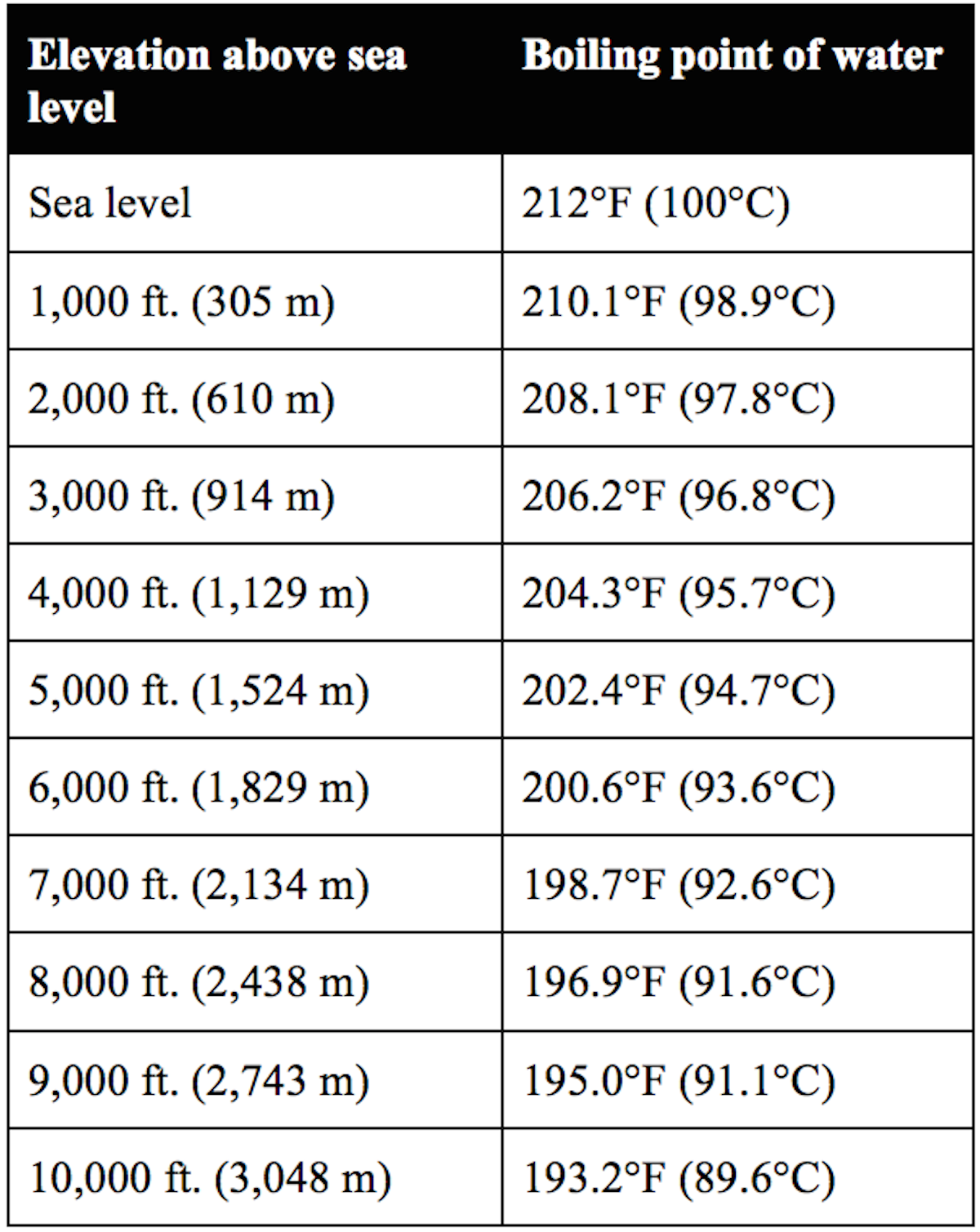
How to Calibrate a Thermometer Craft Beer & Brewing Magazine
THE CALIBRATION FLOW CHART
Calibration charts. (A, B) Calibration chart of 2‐year cumulative CVD... Download Scientific
It Ensures That The Instrument.
The Process Of Comparison Of A Device With Unknown Accuracy To A Device With A Known, Accurate Standard To Eliminate Any Variation In The Device Being Checked Is Called Calibration.
A Person Typically Performs A Calibration To Determine.
Related Post: